Page 8 - Read Online
P. 8
Zhu et al. HA in tissue engineering
Modification site
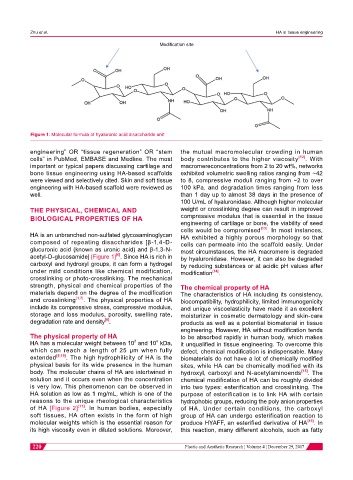
Figure 1: Molecular formula of hyaluronic acid disaccharide unit
engineering” OR “tissue regeneration” OR “stem the mutual macromolecular crowding in human
cells” in PubMed, EMBASE and Medline. The most body contributes to the higher viscosity [12] . With
important or typical papers discussing cartilage and macromereconcentrations from 2 to 20 wt%, networks
bone tissue engineering using HA-based scaffolds exhibited volumetric swelling ratios ranging from ~42
were viewed and selectively cited. Skin and soft tissue to 8, compressive moduli ranging from ~2 to over
engineering with HA-based scaffold were reviewed as 100 kPa, and degradation times ranging from less
well. than 1 day up to almost 38 days in the presence of
100 U/mL of hyaluronidase. Although higher molecular
THE PHYSICAL, CHEMICAL AND weight or crosslinking degree can result in improved
BIOLOGICAL PROPERTIES OF HA compressive modulus that is essential in the tissue
engineering of cartilage or bone, the viability of seed
cells would be compromised [13] . In most instances,
HA is an unbranched non-sulfated glycosaminoglycan HA exhibited a highly porous morphology so that
composed of repeating disaccharides [β-1,4-D- cells can permeate into the scaffold easily. Under
glucuronic acid (known as uronic acid) and β-1,3-N- most circumstances, the HA macromere is degraded
[6]
acetyl-D-glucosamide] [Figure 1] . Since HA is rich in by hyaluronidase. However, it can also be degraded
carboxyl and hydroxyl groups, it can form a hydrogel by reducing substances or at acidic pH values after
under mild conditions like chemical modification, modification [14] .
crosslinking or photo-crosslinking. The mechanical
strength, physical and chemical properties of the The chemical property of HA
materials depend on the degree of the modification The characteristics of HA including its consistency,
and crosslinking [1,7] . The physical properties of HA biocompatibility, hydrophilicity, limited immunogenicity
include its compressive stress, compressive modulus, and unique viscoelasticity have made it an excellent
storage and loss modulus, porosity, swelling rate, moisturizer in cosmetic dermatology and skin-care
[8]
degradation rate and density . products as well as a potential biomaterial in tissue
engineering. However, HA without modification tends
The physical property of HA to be absorbed rapidly in human body, which makes
3
4
HA has a molecular weight between 10 and 10 kDa, it unqualified in tissue engineering. To overcome this
which can reach a length of 25 μm when fully defect, chemical modification is indispensable. Many
extended [9,10] . The high hydrophilicity of HA is the biomaterials do not have a lot of chemically modified
physical basis for its wide presence in the human sites, while HA can be chemically modified with its
body. The molecular chains of HA are intertwined in hydroxyl, carboxyl and N-acetylaminoends [15] . The
solution and it occurs even when the concentration chemical modification of HA can be roughly divided
is very low. This phenomenon can be observed in into two types: esterification and crosslinking. The
HA solution as low as 1 mg/mL, which is one of the purpose of esterification is to link HA with certain
reasons to the unique rheological characteristics hydrophobic groups, reducing the poly anion properties
of HA [Figure 2] [11] . In human bodies, especially of HA. Under certain conditions, the carboxyl
soft tissues, HA often exists in the form of high group of HA can undergo esterification reaction to
molecular weights which is the essential reason for produce HYAFF, an esterified derivative of HA [16] . In
its high viscosity even in diluted solutions. Moreover, this reaction, many different alcohols, such as fatty
220 Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 4 ¦ December 29, 2017