Page 11 - Read Online
P. 11
Page 6 of 15 Sarrami et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2024;11:13 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2024.06
Table 2. Surgical options for autologous breast reconstruction with vascularized lymph node transfer
Donor site
Outcomes Benefits Pitfalls
lymphedema
[29]
DIEP flap with inguinal Mean volume reduction: 10%- Reliable vascular supply to Bipedicle flap design 1.6%
nodes 31% [16,25] flap and lymph nodes Donor site hollowing wound
[16,26]
Discontinuation of compression Large amount of soft tissue breakdown: 16%-20%
therapy: 40%-60% [25,26] for breast reconstruction Donor site seroma: 2%-
[16,25,26]
Reduction of physiotherapy: 12%
[25,26]
60%-100%
LD Flap with lateral Mean volume reduction: 44.4%- Pedicled flap design High overall complication rate: 13.2% [29]
thoracic nodes 48% [4,28] 18.4% [29]
Lymphocele: 2.5% [29]
[29]
SCIP Flap with inguinal Discontinuation of compression Flap harvest does not invade Overall complication rate: 1.6%
nodes therapy (n = 1): 100% [32] underlying fascia 10.9% [29]
Discontinuation of Lymphocele or seroma:
physiotherapy (n = 3): 100% [26] 7.7% [29]
Change in quality-of-life score*
(n = 3): 2% [25,26]
[29,45]
Vascularized omentum Mean volume reduction (n = 7): No disruption of donor site 0%
[44]
lymphatic transfer 0%-77% lymphatic drainage Intra-abdominal surgery
Risk of ileus (2.2%), transient
[45]
pancreatitis (1.1%)
DIEP: deep inferior epigastric perforator; LD: latissimus dorsi; SCIP: superficial circumflex iliac perforator; *: Quality-of-life assessed using Upper
Limb Lymphedema-27 Questionnaire
Figure 5. Preoperative (right) and postoperative (left) images of DIEP flap breast reconstruction with inguinal lymph nodes for the
breast cancer patient with a history of upper extremity lymphedema. DIEP: deep inferior epigastric perforator.
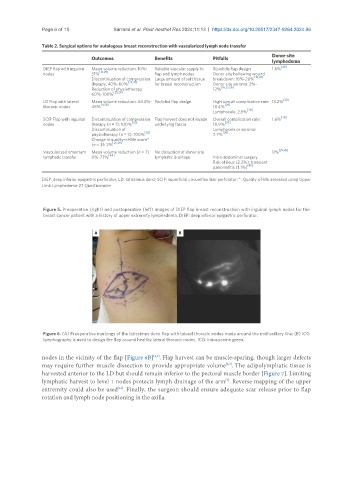
Figure 6. (A) Preoperative markings of the latissimus dorsi flap with lateral thoracic nodes made around the mid-axillary line; (B) ICG
lymphography is used to design the flap around healthy lateral thoracic nodes. ICG: indocyanine green.
nodes in the vicinity of the flap [Figure 6B] . Flap harvest can be muscle-sparing, though larger defects
[4,5]
may require further muscle dissection to provide appropriate volume . The adipolymphatic tissue is
[4,7]
harvested anterior to the LD but should remain inferior to the pectoral muscle border [Figure 7]. Limiting
lymphatic harvest to level 1 nodes protects lymph drainage of the arm . Reverse mapping of the upper
[7]
[18]
extremity could also be used . Finally, the surgeon should ensure adequate scar release prior to flap
rotation and lymph node positioning in the axilla.