Page 12 - Read Online
P. 12
EL-Sabawi et al. Restoration of failed breast reconstruction
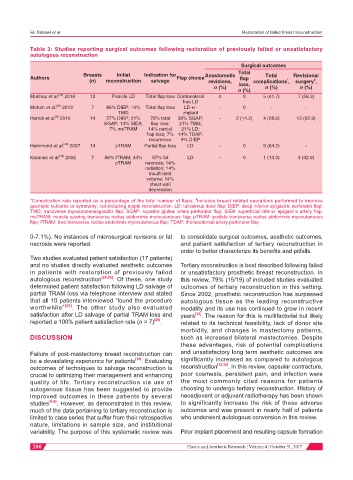
Table 3: Studies reporting surgical outcomes following restoration of previously failed or unsatisfactory
autologous reconstruction
Surgical outcomes
Breasts Initial Indication for Anastomotic Total Total Revisional
Authors Flap choice flap
*
#
(n) reconstruction salvage revisions, complications , surgery ,
n (%) loss, n (%) n (%)
n (%)
Munhoz et al. 2016 12 Pedicle LD Total flap loss Contralateral 0 0 5 (41.7) 7 (58.3)
[16]
free LD
[20]
Mohan et al. 2013 7 86% DIEP; 14% Total flap loss LD +/- - 0 - -
TMG implant
[8]
Hamdi et al. 2010 14 57% DIEP; 21% 79% total 36% SGAP; - 2 (14.2) 4 (28.6) 13 (92.9)
SGAP; 14% SIEA; flap loss; 21% TMG;
7% msTRAM 14% partial 21% LD;
flap loss; 7% 14% TDAP;
recurrence 9% DIEP
[28]
Hammond et al. 2007 14 pTRAM Partial flap loss LD - 0 9 (64.2) -
[29]
Karanas et al. 2002 7 56% fTRAM; 44% 57% fat LD - 0 1 (14.3) 3 (42.9)
pTRAM necrosis; 14%
radiation; 14%
insufficient
volume; 14%
chest wall
depression
#
*Complication rate reported as a percentage of the total number of flaps; includes breast related operations performed to improve
aesthetic outcome or symmetry, not including nipple reconstruction. LD: latissimus dorsi flap; DIEP: deep inferior epigastric perforator flap;
TMG: transverse myocutaneousgracilis flap; SGAP: superior gluteal artery perforator flap; SIEA: superficial inferior epigastric artery flap;
msTRAM: muscle sparing transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap; pTRAM: pedicle transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous
flap; fTRAM: free transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap; TDAP: thoracodorsal artery perforator flap
0-7.1%). No instances of microsurgical revisions or fat to consolidate surgical outcomes, aesthetic outcomes,
necrosis were reported. and patient satisfaction of tertiary reconstruction in
order to better characterize its benefits and pitfalls.
Two studies evaluated patient satisfaction (17 patients)
and no studies directly evaluated aesthetic outcomes Tertiary reconstruction is best described following failed
in patients with restoration of previously failed or unsatisfactory prosthetic breast reconstruction. In
autologous reconstruction [28,29] . Of these, one study this review, 79% (15/19) of included studies evaluated
determined patient satisfaction following LD salvage of outcomes of tertiary reconstruction in this setting.
partial TRAM loss via telephone interview and stated Since 2002, prosthetic reconstruction has surpassed
that all 10 patients interviewed “found the procedure autologous tissue as the leading reconstructive
worthwhile” [28] . The other study also evaluated modality and its use has continued to grow in recent
satisfaction after LD salvage of partial TRAM loss and years [12] . The reason for this is multifactorial but likely
reported a 100% patient satisfaction rate (n = 7) [29] . related to its technical feasibility, lack of donor site
morbidity, and changes in mastectomy patterns,
DISCUSSION such as increased bilateral mastectomies. Despite
these advantages, risk of potential complications
Failure of post-mastectomy breast reconstruction can and unsatisfactory long term aesthetic outcomes are
be a devastating experience for patients [15] . Evaluating significantly increased as compared to autologous
outcomes of techniques to salvage reconstruction is reconstruction [13,30] . In this review, capsular contracture,
crucial to optimizing their management and enhancing poor cosmesis, persistent pain, and infection were
quality of life. Tertiary reconstruction via use of the most commonly cited reasons for patients
autogenous tissue has been suggested to provide choosing to undergo tertiary reconstruction. History of
improved outcomes in these patients by several neoadjuvant or adjuvant radiotherapy has been shown
studies [6-8] . However, as demonstrated in this review, to significantly increase the risk of these adverse
much of the data pertaining to tertiary reconstruction is outcomes and was present in nearly half of patients
limited to case series that suffer from their retrospective who underwent autologous conversion in this review.
nature, limitations in sample size, and institutional
variability. The purpose of this systematic review was Prior implant placement and resulting capsule formation
200 Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 4 ¦ October 31, 2017