Page 11 - Read Online
P. 11
EL-Sabawi et al. Restoration of failed breast reconstruction
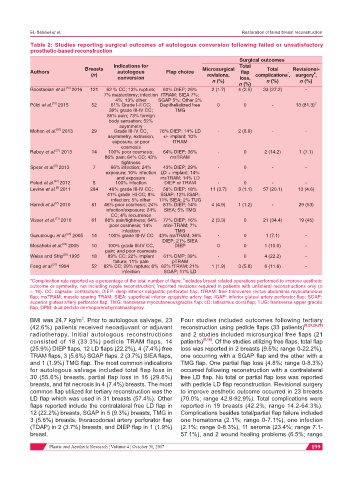
Table 2: Studies reporting surgical outcomes of autologous conversion following failed or unsatisfactory
prosthetic-based reconstruction
Surgical outcomes
Indications for Total
Breasts Microsurgical Total Revisional-
Authors autologous Flap choice flap * #
(n) revisions, complications , surgery ,
conversion loss,
n (%) n (%) n (%)
n (%)
[10]
Roostaeian et al. 2016 121 62 % CC; 13% rupture; 60% DIEP; 26% 2 (1.7) 4 (2.5) 33 (27.2) -
7% mastectomy; infection fTRAM; SIEA 7%;
4%; 13% other SGAP 5%; Other 2%
[18]
Pülzl et al. 2015 52 61% Grade I-II CC; Depithelialized free 0 0 - 13 (81.3) C
39% grade III-IV CC; TMG
85% pain; 73% foreign
body sensation; 52%
asymmetry
[20]
Mohan et al. 2013 29 Grade III-IV CC, 76% DIEP; 14% LD - 2 (6.9) - -
asymmetry, extrusion, +/- implant; 10%
exposure, or poor fTRAM
cosmesis
[21]
Rabey et al. 2013 14 100% poor cosmesis; 64% DIEP; 36% - 0 2 (14.2) 1 (7.1)
86% pain; 64% CC; 43% msTRAM
tightness
[6]
Spear et al. 2013 7 66% infection; 24% 43% DIEP; 29% - 0 - -
exposure; 10% infection LD + implant; 14%
and exposure msTRAM; 14% LD
[22]
Peled et al. 2012 5 100% infection DIEP or TRAM - 0 - -
[9]
Levine et al. 2011 284 46% grade III-IV CC; 58% DIEP; 18% 11 (3.7) 3 (1.1) 57 (20.1) 13 (4.6)
41% grade I-II CC; 8% SGAP; 12% IGAP;
infection; 5% other 11% SIEA; 2% TUG
[7]
Hamdi et al. 2010 81 46% poor cosmesis; 24% 81% DIEP; 14% 4 (4.9) 1 (1.2) - 29 (53)
infection/exposure; 24% SIEA; 5% TMG
CC; 4% recurrence
[11]
Visser et al. 2010 61 68% pain/tightness; 64% 77% DIEP; 16% 2 (3.3) 0 21 (34.4) 19 (45)
poor cosmesis; 14% mini-TRAM; 7%
infection TMG
[23]
Gurunlougu et al. 2005 14 100% grade III-IV CC 43% msTRAM; 36% - 0 1 (7.1) -
DIEP; 21% SIEA
[24]
Mosahebi et al. 2005 10 100% grade III-IV CC, DIEP 0 0 1 (10.0) -
pain; and poor cosmesis
Weiss and Ship 1995 18 89% CC; 22% implant 61% DMP; 39% - 0 4 (22.2) -
[26]
failure; 11% pain pTRAM
[27]
Feng et al. 1994 52 82% CC; 29% rupture; 6% 62% fTRAM; 21% 1 (1.9) 3 (5.8) 6 (11.6) -
infection SGAP; 17% LD
#
*Complication rate reported as a percentage of the total number of flaps; includes breast related operations performed to improve aesthetic
c
outcome or symmetry, not including nipple reconstruction; reported revisions required in patients with unilateral reconstructions only (n
= 16). CC: capsular contracture; DIEP: deep inferior epigastric perforator flap; fTRAM: free transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous
flap; msTRAM, muscle sparing TRAM; SIEA: superficial inferior epigastric artery flap; IGAP: inferior gluteal artery perforator flap; SGAP:
superior gluteal artery perforator flap; TMG: transverse myocutaneousgracilis flap; LD: latissimus dorsi flap; TUG: transverse upper gracilis
flap; DPM: dual pedicle dermoparenchymalmastopexy
2
BMI was 24.7 kg/m . Prior to autologous salvage, 23 Four studies included outcomes following tertiary
(42.6%) patients received neoadjuvant or adjuvant reconstruction using pedicle flaps (33 patients) [8,20,28,29]
radiotherapy. Initial autologous reconstructions and 2 studies included microsurgical free flaps (21
consisted of 18 (33.3%) pedicle TRAM flaps, 14 patients) [8,16] . Of the studies utilizing free flaps, total flap
(25.9%) DIEP flaps, 12 LD flaps (22.2%), 4 (7.4%) free loss was reported in 2 breasts (9.5%; range 0-22.2%),
TRAM flaps, 3 (5.6%) SGAP flaps, 2 (3.7%) SIEA flaps, one occurring with a SGAP flap and the other with a
and 1 (1.9%) TMG flap. The most common indications TMG flap. One partial flap loss (4.8%; range 0-8.3%)
for autologous salvage included total flap loss in occurred following reconstruction with a contralateral
30 (55.6%) breasts, partial flap loss in 16 (29.6%) free LD flap. No total or partial flap loss was reported
breasts, and fat necrosis in 4 (7.4%) breasts. The most with pedicle LD flap reconstruction. Revisional surgery
common flap utilized for tertiary reconstruction was the to improve aesthetic outcome occurred in 23 breasts
LD flap which was used in 31 breasts (57.4%). Other (70.0%; range 42.8-92.9%). Total complications were
flaps reported include the contralateral free LD flap in reported in 19 breasts (42.2%; range 14.2-64.3%).
12 (22.2%) breasts, SGAP in 5 (9.3%) breasts, TMG in Complications besides total/partial flap failure included
3 (5.6%) breasts, thoracodorsal artery perforator flap one hematoma (2.1%; range 0-7.1%), one infection
(TDAP) in 2 (3.7%) breasts, and DIEP flap in 1 (1.9%) (2.1%; range 0-8.3%), 11 seroma (23.4%; range 7.1-
breast. 57.1%), and 2 wound healing problems (6.5%; range
Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 4 ¦ October 31, 2017 199