Page 15 - Read Online
P. 15
Liu et al. Inflatable pressure garment device
A B
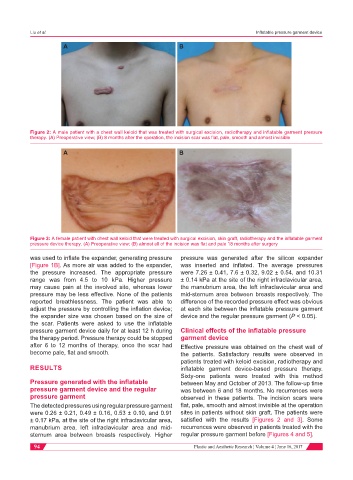
Figure 2: A male patient with a chest wall keloid that was treated with surgical excision, radiotherapy and inflatable garment pressure
therapy. (A) Preoperative view; (B) 8 months after the operation, the incision scar was flat, pale, smooth and almost invisible
A B
Figure 3: A female patient with chest wall keloid that were treated with surgical excision, skin graft, radiotherapy and the inflatable garment
pressure device therapy. (A) Preoperative view; (B) almost all of the incision was flat and pale 18 months after surgery
was used to inflate the expander, generating pressure pressure was generated after the silicon expander
[Figure 1B]. As more air was added to the expander, was inserted and inflated. The average pressures
the pressure increased. The appropriate pressure were 7.26 ± 0.41, 7.6 ± 0.32, 9.02 ± 0.54, and 10.31
range was from 4.5 to 10 kPa. Higher pressure ± 0.14 kPa at the site of the right infraclavicular area,
may cause pain at the involved site, whereas lower the manubrium area, the left infraclavicular area and
pressure may be less effective. None of the patients mid-sternum area between breasts respectively. The
reported breathlessness. The patient was able to difference of the recorded pressure effect was obvious
adjust the pressure by controlling the inflation device; at each site between the inflatable pressure garment
the expander size was chosen based on the size of device and the regular pressure garment (P < 0.05).
the scar. Patients were asked to use the inflatable
pressure garment device daily for at least 12 h during Clinical effects of the inflatable pressure
the therapy period. Pressure therapy could be stopped garment device
after 6 to 12 months of therapy, once the scar had Effective pressure was obtained on the chest wall of
become pale, flat and smooth. the patients. Satisfactory results were observed in
patients treated with keloid excision, radiotherapy and
RESULTS inflatable garment device-based pressure therapy.
Sixty-one patients were treated with this method
Pressure generated with the inflatable between May and October of 2013. The follow-up time
pressure garment device and the regular was between 6 and 18 months. No recurrences were
pressure garment observed in these patients. The incision scars were
The detected pressures using regular pressure garment flat, pale, smooth and almost invisible at the operation
were 0.26 ± 0.21, 0.49 ± 0.16, 0.53 ± 0.10, and 0.91 sites in patients without skin graft. The patients were
± 0.17 kPa, at the site of the right infraclavicular area, satisfied with the results [Figures 2 and 3]. Some
manubrium area, left infraclavicular area and mid- recurrences were observed in patients treated with the
sternum area between breasts respectively. Higher regular pressure garment before [Figures 4 and 5].
94 Plastic and Aesthetic Research ¦ Volume 4 ¦ June 16, 2017