Page 98 - Read Online
P. 98
Page 10 of 13 Myers et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2023;10:38 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2022.150
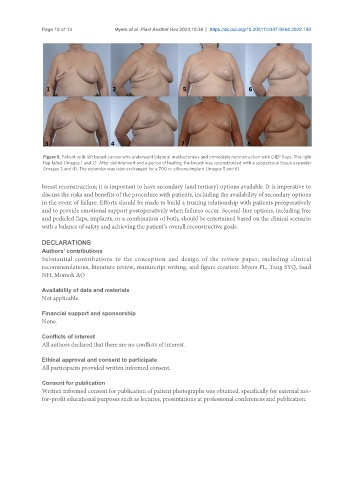
Figure 5. Patient with left breast cancer who underwent bilateral mastectomies and immediate reconstruction with DIEP flaps. The right
flap failed (Images 1 and 2). After debridement and a period of healing, the breast was reconstructed with a subpectoral tissue expander
(Images 3 and 4). The expander was later exchanged for a 700 cc silicone implant (Images 5 and 6).
breast reconstruction; it is important to have secondary (and tertiary) options available. It is imperative to
discuss the risks and benefits of the procedure with patients, including the availability of secondary options
in the event of failure. Efforts should be made to build a trusting relationship with patients preoperatively
and to provide emotional support postoperatively when failures occur. Second-line options, including free
and pedicled flaps, implants, or a combination of both, should be entertained based on the clinical scenario
with a balance of safety and achieving the patient’s overall reconstructive goals.
DECLARATIONS
Authors’ contributions
Substantial contributions to the conception and design of the review paper, including clinical
recommendations, literature review, manuscript writing, and figure creation: Myers PL, Tang SYQ, Saad
NH, Momoh AO
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Financial support and sponsorship
None.
Conflicts of interest
All authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
All participants provided written informed consent.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication of patient photographs was obtained, specifically for external not-
for-profit educational purposes such as lectures, presentations at professional conferences and publication.