Page 16 - Read Online
P. 16
Chen et al. Plast Aesthet Res 2023;10:24 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-9264.2022.136 Page 7 of 26
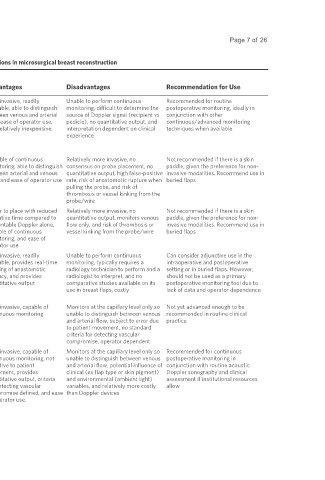
Table 1. Intra- and postoperative monitoring techniques for the detection of thrombotic complications in microsurgical breast reconstruction
Flap Monitoring Mechanism of Monitoring Receiver Operating Advantages Disadvantages Recommendation for Use
Technique Characteristics
Acoustic Doppler The location of the arterial and venous Sensitivity: 50% Non-invasive, readily Unable to perform continuous Recommended for routine
[77]
Sonography anastomoses is marked on the surface of Specificity: 100% available, able to distinguish monitoring, difficult to determine the postoperative monitoring, ideally in
the flap intraoperatively. A Doppler PPV: 100% between venous and arterial source of Doppler signal (recipient vs conjunction with other
probe is placed on the surface of the skin NPV: 98.6% flow, ease of operator use, pedicle), no quantitative output, and continuous/advanced monitoring
paddle overlying the vessel. An auditory Accuracy: 98.6% and relatively inexpensive. interpretation dependent on clinical techniques when available
pulsatile or continuous hum sound SR: 100% experience
confirms arterial or venous patency,
respectively
Cook-Swartz An electrode mounted on a silicone cuff Sensitivity: 100% Capable of continuous Relatively more invasive, no Not recommended if there is a skin
Implantable Doppler is secured around the vascular pedicle Specificity: 88-100% monitoring, able to distinguish consensus on probe placement, no paddle, given the preference for non-
[162-168]
with a thin wire connecting it to an PPV: 33.3-100% between arterial and venous quantitative output, high false-positive invasive modalities. Recommend use in
external monitor. Auditory output is NPV: 100% flow, and ease of operator use rate, risk of anastomotic rupture when buried flaps
similar to that of acoustic Doppler Accuracy: 88.7-100% pulling the probe, and risk of
sonography SR: 80-100% thrombosis or vessel kinking from the
probe/wire
Flow Coupler A venous coupler is fitted with a Doppler Sensitivity: 100% Easier to place with reduced Relatively more invasive, no Not recommended if there is a skin
Implantable Doppler probe with a thin wire connecting it to an Specificity: 94-98.1% operative time compared to quantitative output, monitors venous paddle, given the preference for non-
[162,169]
external monitor. Auditory output is PPV: 60-66.7% implantable Doppler alone, flow only, and risk of thrombosis or invasive modalities. Recommend use in
similar to that of acoustic Doppler NPV: 100% capable of continuous vessel kinking from the probe/wire buried flaps
sonography Accuracy: 94.7-98.2% monitoring, and ease of
SR: 75-100% operator use
Color Duplex An ultrasound probe and viewing Receiver operating characteristics Non-invasive, readily Unable to perform continuous Can consider adjunctive use in the
Ultrasonography [170, monitor allows direct visualization of for the detection of microvascular available, provides real-time monitoring, typically requires a intraoperative and postoperative
171]
vessel patency as well as blood flow thrombosis have not been reported imaging of anastomotic radiology technician to perform and a setting or in buried flaps. However,
velocity and direction in the context of microsurgical patency, and provides radiologist to interpret, and no should not be used as a primary
breast reconstruction; however, quantitative output comparative studies available on its postoperative monitoring tool due to
Jacob et al. and Arya et al. have use in breast flaps, costly lack of data and operator dependence
described its potential use
Laser Doppler A probe attached to the surface of the Sensitivity: 100% Non-invasive, capable of Monitors at the capillary level only so Not yet advanced enough to be
[172]
Flowmetry skin paddle emits laser light which is Specificity: 100% continuous monitoring unable to distinguish between venous recommended in routine clinical
reflected back by the movement of red PPV: 100% and arterial flow, subject to error due practice
blood cells to calculate their velocity NPV: 100% to patient movement, no standard
Accuracy: 100% criteria for detecting vascular
SR: 80% compromise, operator dependent
Near-Infrared and A probe attached to the surface of the Sensitivity: 96.5-100% Non-invasive, capable of Monitors at the capillary level only so Recommended for continuous
Visible Light skin paddle emits near-infrared or visible Specificity: 96.4-100% continuous monitoring, not unable to distinguish between venous postoperative monitoring in
[77,81-83,
Spectroscopy light, which is absorbed by PPV: 50-100% sensitive to patient and arterial flow, potential influence of conjunction with routine acoustic
172-179]
chromophores (oxygenated and NPV: 99.8-100% movement, provides clinical (ex flap type or skin pigment) Doppler sonography and clinical
deoxygenated hemoglobin). The Accuracy: 97-100% quantitative output, criteria and environmental (ambient light) assessment if institutional resources
reduction in light intensity is measured SR: 66.7-100% for detecting vascular variables, and relatively more costly allow
to determine tissue oxygen saturation compromise defined, and ease than Doppler devices
of operator use.