Page 85 - Read Online
P. 85
Millien et al. One Health Implement Res 2023;3:148-60 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ohir.2023.37 Page 152
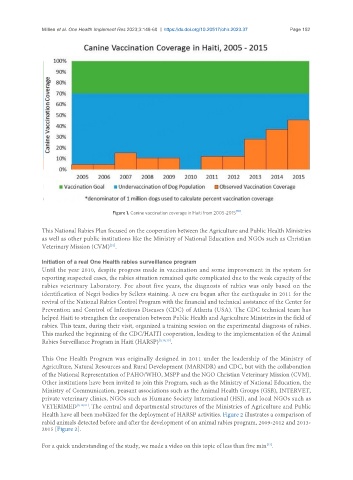
Figure 1. Canine vaccination coverage in Haiti from 2005-2015 [18] .
This National Rabies Plan focused on the cooperation between the Agriculture and Public Health Ministries
as well as other public institutions like the Ministry of National Education and NGOs such as Christian
[21]
Veterinary Mission (CVM) .
Initiation of a real One Health rabies surveillance program
Until the year 2010, despite progress made in vaccination and some improvement in the system for
reporting suspected cases, the rabies situation remained quite complicated due to the weak capacity of the
rabies veterinary Laboratory. For about five years, the diagnosis of rabies was only based on the
identification of Negri bodies by Sellers staining. A new era began after the earthquake in 2011 for the
revival of the National Rabies Control Program with the financial and technical assistance of the Center for
Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases (CDC) of Atlanta (USA). The CDC technical team has
helped Haiti to strengthen the cooperation between Public Health and Agriculture Ministries in the field of
rabies. This team, during their visit, organized a training session on the experimental diagnosis of rabies.
This marked the beginning of the CDC/HAITI cooperation, leading to the implementation of the Animal
Rabies Surveillance Program in Haiti (HARSP) [9,18,19] .
This One Health Program was originally designed in 2011 under the leadership of the Ministry of
Agriculture, Natural Resources and Rural Development (MARNDR) and CDC, but with the collaboration
of the National Representation of PAHO/WHO, MSPP and the NGO Christian Veterinary Mission (CVM).
Other institutions have been invited to join this Program, such as the Ministry of National Education, the
Ministry of Communication, peasant associations such as the Animal Health Groups (GSB), INTERVET,
private veterinary clinics, NGOs such as Humane Society International (HSI), and local NGOs such as
VETERIMED [9,18,21] . The central and departmental structures of the Ministries of Agriculture and Public
Health have all been mobilized for the deployment of HARSP activities. Figure 2 illustrates a comparison of
rabid animals detected before and after the development of an animal rabies program, 2009-2012 and 2013-
2015 [Figure 2].
[22]
For a quick understanding of the study, we made a video on this topic of less than five min .