Page 73 - Read Online
P. 73
Page 140 Akanbi et al. One Health Implement Res 2023;3:135-47 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ohir.2023.29
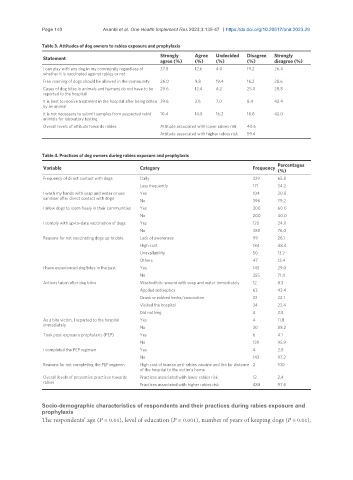
Table 3. Attitudes of dog owners to rabies exposure and prophylaxis
Strongly Agree Undecided Disagree Strongly
Statement
agree (%) (%) (%) (%) disagree (%)
I can play with any dog in my community regardless of 37.8 12.6 4.0 19.2 26.4
whether it is vaccinated against rabies or not
Free roaming of dogs should be allowed in the community 26.0 9.8 19.4 16.2 28.6
Cases of dog bites in animals and humans do not have to be 29.6 12.4 4.2 25.0 28.8
reported to the hospital
It is best to receive treatment in the hospital after being bitten 39.6 2.6 7.0 8.4 42.4
by an animal
It is not necessary to submit samples from suspected rabid 10.4 14.8 16.2 16.6 42.0
animals for laboratory testing
Overall levels of attitude towards rabies Attitude associated with lower rabies risk 40.6
Attitude associated with higher rabies risk 59.4
Table 4. Practices of dog owners during rabies exposure and prophylaxis
Variable Category Frequency Percentages
(%)
Frequency of direct contact with dogs Daily 329 65.8
Less frequently 171 34.2
I wash my hands with soap and water or use Yes 104 20.8
sanitiser after direct contact with dogs
No 396 79.2
I allow dogs to roam freely in their communities Yes 300 60.0
No 200 40.0
I comply with up-to-date vaccination of dogs Yes 120 24.0
No 380 76.0
Reasons for not vaccinating dogs up to date Lack of awareness 99 26.1
High cost 184 48.4
Unavailability 50 13.2
Others 47 12.4
I have experienced dog bites in the past Yes 145 29.0
No 355 71.0
Actions taken after dog bites Washed bite wound with soap and water immediately 12 8.3
Applied antiseptics 63 43.4
Drank or rubbed herbs/concoction 32 22.1
Visited the hospital 34 23.4
Did nothing 4 2.8
As a bite victim, I reported to the hospital Yes 4 11.8
immediately
No 30 88.2
Took post-exposure prophylaxis (PEP) Yes 6 4.1
No 139 95.9
I completed the PEP regimen Yes 4 2.8
No 143 97.2
Reasons for not completing the PEP regimen High cost of human anti-rabies vaccine and the far distance 2 100
of the hospital to the victim’s home
Overall levels of preventive practices towards Practices associated with lower rabies risk 12 2.4
rabies
Practices associated with higher rabies risk 488 97.6
Socio-demographic characteristics of respondents and their practices during rabies exposure and
prophylaxis
The respondents’ age (P = 0.01), level of education (P = 0.001), number of years of keeping dogs (P = 0.01),