Page 116 - Read Online
P. 116
Page 294 Nociti. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 2020;7:291-9 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-8659.2020.25
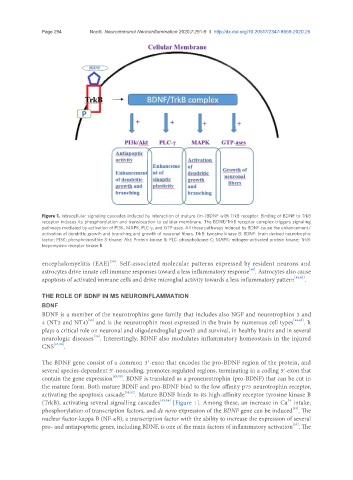
Figure 1. Intracellular signaling cascades induced by interaction of mature (m-)BDNF with TrkB receptor. Binding of BDNF to TrkB
receptor induces its phosphorylation and translocation to cellular membrane. The BDNF/TrkB receptor complex triggers signaling
pathways mediated by activation of PI3K, MAPK, PLC-γ, and GTP-ases. All these pathways induced by BDNF cause the enhancement/
activation of dendritic growth and branching and growth of neuronal fibers. TrkB: tyrosine kinase B; BDNF: brain derived neurotrophic
factor; PI3K: phosphoinositide 3-kinase; Akt: Protein kinase B; PLC: phospholipase C; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; TrkB:
tropomyosin receptor kinase B
[39]
encephalomyelitis (EAE) . Self-associated molecular patterns expressed by resident neurons and
[40]
astrocytes drive innate cell immune responses toward a less inflammatory response . Astrocytes also cause
apoptosis of activated immune cells and drive microglial activity towards a less inflammatory pattern [41,42] .
THE ROLE OF BDNF IN MS NEUROINFLAMMATION
BDNF
BDNF is a member of the neurotrophins gene family that includes also NGF and neurotrophins 3 and
[43]
4 (NT3 and NT4) and is the neurotrophin most expressed in the brain by numerous cell types [44,45] . It
plays a critical role on neuronal and oligodendroglial growth and survival, in healthy brains and in several
[46]
neurologic diseases . Interestingly, BDNF also modulates inflammatory homeostasis in the injured
CNS [47,48] .
The BDNF gene consist of a common 3′-exon that encodes the pro-BDNF region of the protein, and
several species-dependent 5′-noncoding, promoter-regulated regions, terminating in a coding 5′-exon that
contain the gene expression [49,50] . BDNF is translated as a proneurotrophin (pro-BDNF) that can be cut in
the mature form. Both mature BDNF and pro-BDNF bind to the low affinity p75 neurotrophin receptor,
activating the apoptosis cascade [51,52] . Mature BDNF binds to its high-affinity receptor tyrosine kinase B
2+
(TrkB), activating several signalling cascades [53,54] [Figure 1]. Among these, an increase in Ca intake,
phosphorylation of transcription factors, and de novo expression of the BDNF gene can be induced . The
[53]
nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB), a transcription factor with the ability to increase the expression of several
[55]
pro- and antiapoptotic genes, including BDNF, is one of the main factors of inflammatory activation . The