Page 9 - Read Online
P. 9
Page 4 of 12 Zheng et al. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 2019;6:1 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-8659.2018.52
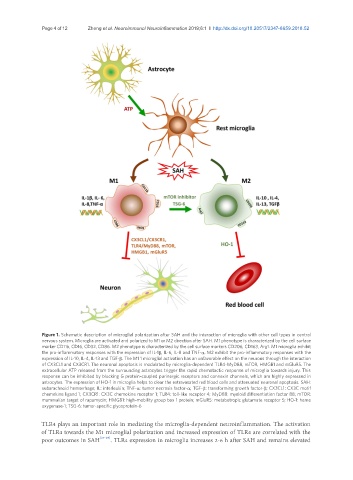
Figure 1. Schematic description of microglial polarization after SAH and the interaction of microglia with other cell types in central
nervous system. Microglia are activated and polarized to M1 or M2 direction after SAH. M1 phenotype is characterized by the cell surface
marker CD11b, CD16, CD32, CD86. M2 phenotype is characterized by the cell surface markers CD206, CD163, Arg1. M1 microglia exhibit
the pro-inflammatory responses with the expression of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-α. M2 exhibit the pro-inflammatory responses with the
expression of IL-10, IL-4, IL-13 and TGF-β. The M1 1 microglial activation has an unfavorable effect on the neurons through the interaction
of CX3CL1 and CX3CR1. The neuronal apoptosis is modulated by microglia-dependent TLR4-MyD88, mTOR, HMGB1 and mGluR5. The
extracellular ATP released from the surrounding astrocytes trigger the rapid chemotactic response of microglia towards injury. This
response can be inhibited by blocking G protein-coupled purinergic receptors and connexin channels, which are highly expressed in
astrocytes. The expression of HO-1 in microglia helps to clear the extravasated red blood cells and attenuated neuronal apoptosis. SAH:
subarachnoid hemorrhage; IL: interleukin; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α; TGF-β: transforming growth factor-β; CX3CL1: CX3C motif
chemokine ligand 1; CX3CR1: CX3C chemokine receptor 1; TLR4: toll-like receptor 4; MyD88: myeloid differentiation factor 88; mTOR:
mammalian target of rapamycin; HMGB1: high-mobility group box 1 protein; mGluR5: metabotropic glutamate receptor 5; HO-1: heme
oxygenase-1; TSG-6: tumor-specific glycoprotein-6
TLR4 plays an important role in mediating the microglia-dependent neuroinflammation. The activation
of TLR4 towards the M1 microglial polarization and increased expression of TLR4 are correlated with the
poor outcomes in SAH [37-39] . TLR4 expression in microglia increases 2-6 h after SAH and remains elevated