Page 11 - Read Online
P. 11
Page 6 of 12 Zheng et al. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 2019;6:1 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-8659.2018.52
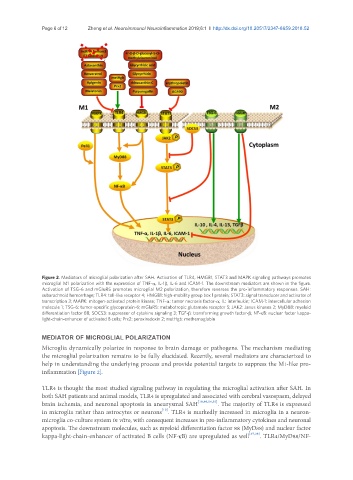
Figure 2. Mediators of microglial polarization after SAH. Activation of TLR4, HMGB1, STAT3 and MAPK signaling pathways promotes
microglial M1 polarization with the expression of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 and ICAM-1. The downstream mediators are shown in the figure.
Activation of TSG-6 and mGluR5 promotes microglial M2 polarization, therefore reverses the pro-inflammatory responses. SAH:
subarachnoid hemorrhage; TLR4: toll-like receptor 4; HMGB1: high-mobility group box 1 protein; STAT3: signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3; MAPK: mitogen-activated protein kinase; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α; IL: interleukin; ICAM-1: intercellular adhesion
molecule 1; TSG-6: tumor-specific glycoprotein-6; mGluR5: metabotropic glutamate receptor 5; JAK2: Janus kinases 2; MyD88: myeloid
differentiation factor 88; SOCS3: suppressor of cytokine signaling 3; TGF-β: transforming growth factor-β; NF-κB: nuclear factor kappa-
light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; Prx2: peroxiredoxin 2; metHgb: methemoglobin
MEDIATOR OF MICROGLIAL POLARIZATION
Microglia dynamically polarize in response to brain damage or pathogens. The mechanism mediating
the microglial polarization remains to be fully elucidated. Recently, several mediators are characterized to
help in understanding the underlying process and provide potential targets to suppress the M1-like pro-
inflammation [Figure 2].
TLR4 is thought the most studied signaling pathway in regulating the microglial activation after SAH. In
both SAH patients and animal models, TLR4 is upregulated and associated with cerebral vasospasm, delayed
brain ischemia, and neuronal apoptosis in aneurysmal SAH [10,40,54,55] . The majority of TLR4 is expressed
[10]
in microglia rather than astrocytes or neurons . TLR4 is markedly increased in microglia in a neuron-
microglia co-culture system in vitro, with consequent increases in pro-inflammatory cytokines and neuronal
apoptosis. The downstream molecules, such as myeloid differentiation factor 88 (MyD88) and nuclear factor
kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) are upregulated as well [37,38] . TLR4/MyD88/NF-