Page 142 - Read Online
P. 142
Page 8 of 13 Alsulihem et al. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 2019;6:13 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-8659.2019.007
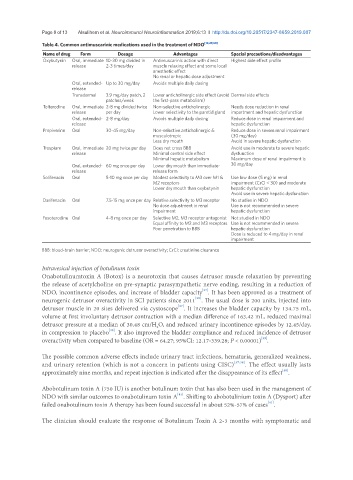
Table 4. Common antimuscarinic medications used in the treatment of NDO [12,29,60]
Name of drug Form Dosage Advantages Special precautions/disadvantages
Oxybutynin Oral, immediate 10-30 mg divided in Antimuscarinic action with direct Highest side effect profile
release 2-3 times/day muscle relaxing effect and some local
anesthetic effect
No renal or hepatic dose adjustment
Oral, extended- Up to 30 mg/day Avoids multiple daily dosing
release
Transdermal 3.9 mg/day patch, 2 Lower anticholinergic side effect (avoid Dermal side effects
patches/week the first-pass metabolism)
Tolterodine Oral, immediate 2-8 mg divided twice Non-selective anticholinergic Needs dose reduction in renal
release per day Lower selectivity to the parotid gland impartment and hepatic dysfunction
Oral, extended- 2-8 mg/day Avoids multiple daily dosing Reduce dose in renal impairment and
release hepatic dysfunction
Propiverine Oral 30-45 mg/day Non-selective anticholinergic & Reduce dose in severe renal impairment
musculotropic (30 mg/day)
Less dry mouth Avoid in severe hepatic dysfunction
Trospium Oral, immediate 20 mg twice per day Does not cross BBB Avoid use in moderate to severe hepatic
release Minimal central side effect dysfunction
Minimal hepatic metabolism Maximum dose of renal impairment is
Oral, extended- 60 mg once per day Lower dry mouth than immediate- 30 mg/day
release release form
Solifenacin Oral 5-10 mg once per day Modest selectivity to M3 over M1 & Use low dose (5 mg) in renal
M2 receptors impairment (CrCl < 30) and moderate
Lower dry mouth than oxybutynin hepatic dysfunction
Avoid use in severe hepatic dysfunction
Darifenacin Oral 7.5-15 mg once per day Relative selectivity to M3 receptor No studies in NDO
No dose adjustment in renal Use is not recommended in severe
impairment hepatic dysfunction
Fesoterodine Oral 4-8 mg once per day Selective M2, M3 receptor antagonist Not studied in NDO
Equal affinity to M2 and M3 receptors Use is not recommended in severe
Poor penetration to BBB hepatic dysfunction
Dose is reduced to 4 mg/day in renal
impairment
BBB: blood-brain barrier; NDO: neurogenic detrusor overactivity; CrCl: creatinine clearance
Intravesical injection of botulinum toxin
Onabotulinumtoxin A (Botox) is a neurotoxin that causes detrusor muscle relaxation by preventing
the release of acetylcholine on pre-synaptic parasympathetic nerve ending, resulting in a reduction of
NDO, incontinence episodes, and increase of bladder capacity . It has been approved as a treatment of
[37]
[38]
neurogenic detrusor overactivity in SCI patients since 2011 . The usual dose is 200 units, injected into
detrusor muscle in 20 sites delivered via cystoscope . It increases the bladder capacity by 134.75 mL,
[37]
volume at first involuntary detrusor contraction with a median difference of 163.42 mL, reduced maximal
detrusor pressure at a median of 30.48 cm/H O, and reduced urinary incontinence episodes by 12.45/day,
2
[39]
in compression to placebo . It also improved the bladder compliance and reduced incidence of detrusor
[39]
overactivity when compared to baseline (OR = 64.27; 95%CI: 12.17-339.28; P < 0.00001) .
The possible common adverse effects include urinary tract infections, hematuria, generalized weakness,
and urinary retention (which is not a concern in patients using CISC) [37,38] . The effect usually lasts
approximately nine months, and repeat injection is indicated after the disappearance of its effect .
[40]
Abobotulinum toxin A (750 IU) is another botulinum toxin that has also been used in the management of
[41]
NDO with similar outcomes to onabotulinum toxin A . Shifting to abobotulinium toxin A (Dysport) after
[41]
failed onabotulinum toxin A therapy has been found successful in about 52%-57% of cases .
The clinician should evaluate the response of Botulinum Toxin A 2-3 months with symptomatic and