Page 309 - Read Online
P. 309
Toyoda. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 2018;5:40 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-8659.2018.48 Page 3 of 8
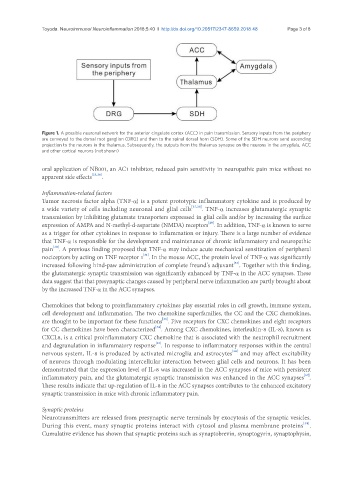
Figure 1. A possible neuronal network for the anterior cingulate cortex (ACC) in pain transmission. Sensory inputs from the periphery
are conveyed to the dorsal root ganglion (DRG) and then to the spinal dorsal horn (SDH). Some of the SDH neurons send ascending
projection to the neurons in the thalamus. Subsequently, the outputs from the thalamus synapse on the neurons in the amygdala, ACC
and other cortical neurons (not shown)
oral application of NB001, an AC1 inhibitor, reduced pain sensitivity in neuropathic pain mice without no
apparent side effects [25,26] .
Inflammation-related factors
Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) is a potent prototypic inflammatory cytokine and is produced by
a wide variety of cells including neuronal and glial cells [27,28] . TNF-α increases glutamatergic synaptic
transmission by inhibiting glutamate transporters expressed in glial cells and/or by increasing the surface
[29]
expression of AMPA and N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptors . In addition, TNF-α is known to serve
as a trigger for other cytokines in response to inflammation or injury. There is a large number of evidence
that TNF-α is responsible for the development and maintenance of chronic inflammatory and neuropathic
[30]
pain . A previous finding proposed that TNF-α may induce acute mechanical sensitization of peripheral
[31]
nociceptors by acting on TNF receptor 1 . In the mouse ACC, the protein level of TNF-α was significantly
[32]
increased following hind-paw administration of complete freund’s adjuvant . Together with this finding,
the glutamatergic synaptic transmission was significantly enhanced by TNF-α in the ACC synapses. These
data suggest that that presynaptic changes caused by peripheral nerve inflammation are partly brought about
by the increased TNF-α in the ACC synapses.
Chemokines that belong to proinflammatory cytokines play essential roles in cell growth, immune system,
cell development and inflammation. The two chemokine superfamilies, the CC and the CXC chemokines,
[33]
are thought to be important for these functions . Five receptors for CXC chemokines and eight receptors
[34]
for CC chemokines have been characterized . Among CXC chemokines, interleukin-8 (IL-8), known as
CXCL8, is a critical proinflammatory CXC chemokine that is associated with the neutrophil recruitment
[35]
and degranulation in inflammatory response . In response to inflammatory responses within the central
[36]
nervous system, IL-8 is produced by activated microglia and astrocytes and may affect excitability
of neurons through modulating intercellular interaction between glial cells and neurons. It has been
demonstrated that the expression level of IL-8 was increased in the ACC synapses of mice with persistent
[37]
inflammatory pain, and the glutamatergic synaptic transmission was enhanced in the ACC synapses .
These results indicate that up-regulation of IL-8 in the ACC synapses contributes to the enhanced excitatory
synaptic transmission in mice with chronic inflammatory pain.
Synaptic proteins
Neurotransmitters are released from presynaptic nerve terminals by exocytosis of the synaptic vesicles.
[38]
During this event, many synaptic proteins interact with cytosol and plasma membrane proteins .
Cumulative evidence has shown that synaptic proteins such as synaptobrevin, synaptogyrin, synaptophysin,