Page 225 - Read Online
P. 225
Page 2 of 7 Chen et al. Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation 2018;5:31 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2347-8659.2018.23
A B C
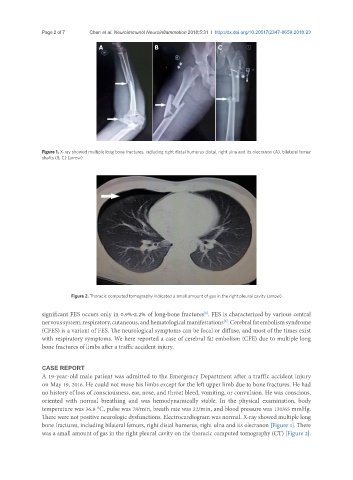
Figure 1. X-ray showed multiple long bone fractures, including right distal humerus distal, right ulna and its olecranon (A), bilateral femur
shafts (B, C) (arrow)
Figure 2. Thoracic computed tomography indicated a small amount of gas in the right pleural cavity (arrow)
significant FES occurs only in 0.9%-2.2% of long-bone fractures . FES is characterized by various central
[1]
nervous system, respiratory, cutaneous, and hematological manifestations . Cerebral fat embolism syndrome
[2]
(CFES) is a variant of FES. The neurological symptoms can be focal or diffuse, and most of the times exist
with respiratory symptoms. We here reported a case of cerebral fat embolism (CFE) due to multiple long
bone fractures of limbs after a traffic accident injury.
CASE REPORT
A 19-year-old male patient was admitted to the Emergency Department after a traffic accident injury
on May 19, 2016. He could not move his limbs except for the left upper limb due to bone fractures. He had
no history of loss of consciousness, ear, nose, and throat bleed, vomiting, or convulsion. He was conscious,
oriented with normal breathing and was hemodynamically stable. In the physical examination, body
temperature was 36.8 °C, pulse was 78/min, breath rate was 22/min, and blood pressure was 130/65 mmHg.
There were not positive neurologic dysfunctions. Electrocardiogram was normal. X-ray showed multiple long
bone fractures, including bilateral femurs, right distal humerus, right ulna and its olecranon [Figure 1]. There
was a small amount of gas in the right pleural cavity on the thoracic computed tomography (CT) [Figure 2].