Page 265 - Read Online
P. 265
Burns et al. Altered filamin A enables Aβ signaling
has not been elucidated. The tau proteopathy in AD,
therefore, involves hyperphosphorylation, but may or
may not include misfolding. The formation of PHFs
requires hyperphosphorylated tau, and tau protein in
neurofibrillary tangles is hyperphosphorylated, most
notably at Ser 202 , Thr 231 and Thr 181[41] . Interestingly,
the alpha-synuclein that forms fibrils and is abundant
in Lewy bodies in Parkinson’s disease is also
hyperphosphorylated, at a single serine site [42] .
ALTERED FLNA LINKS Aβ AND TAU
PROTEOPATHIES
We recently described a third, atypical proteopathy in
AD that is critically interconnected with the toxicities
of both Aβ 42 and tau. This third proteopathy is an
altered conformation of the scaffolding protein FLNA.
It is induced by Aβ 42 , and in reciprocal action, enables
Aβ 42 ’s toxic signaling via α7nAChR to activate kinases
that hyperphosphorylate tau [13] . Altered FLNA enables
N N Aβ 42 ’s signaling via α7nAChR by associating with this
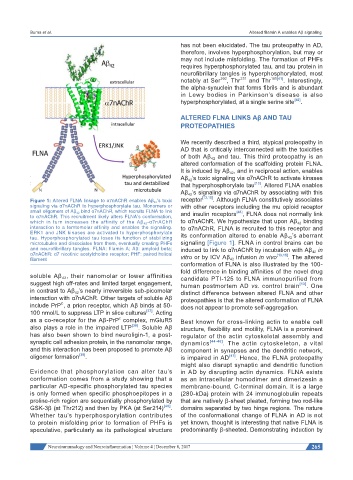
Figure 1: Altered FLNA linkage to α7nAChR enables Aβ 42 ’s toxic receptor [13,15] . Although FLNA constitutively associates
signaling via α7nAChR to hyperphosphorylate tau. Monomers or with other receptors including the mu opioid receptor
small oligomers of Aβ 42 bind α7nAChR, which recruits FLNA to link and insulin receptors [43] , FLNA does not normally link
to α7nAChR. This recruitment likely alters FLNA’s conformation,
which in turn increases the affinity of the Aβ 42 -α7nAChR to α7nAChR. We hypothesize that upon Aβ 42 binding
interaction to a femtomolar affinity and enables the signaling. to α7nAChR, FLNA is recruited to this receptor and
ERK1 and JNK kinases are activated to hyperphosphorylate its conformation altered to enable Aβ 42 ’s aberrant
tau. Hyperphosphorylated tau loses its function of stabilizing
microtubules and dissociates from them, eventually creating PHFs signaling [Figure 1]. FLNA in control brains can be
and neurofibrillary tangles. FLNA: filamin A; Aβ: amyloid beta; induced to link to α7nAChR by incubation with Aβ 42 in
α7nAChR: α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor; PHF: paired helical vitro or by ICV Aβ 42 infusion in vivo [13,15] . The altered
filament
conformation of FLNA is also illustrated by the 100-
fold difference in binding affinities of the novel drug
soluble Aβ 42 , their nanomolar or lower affinities candidate PTI-125 to FLNA immunopurified from
suggest high off-rates and limited target engagement, human postmortem AD vs. control brain [13] . One
in contrast to Aβ 42 ’s nearly irreversible sub-picomolar distinct difference between altered FLNA and other
interaction with α7nAChR. Other targets of soluble Aβ proteopathies is that the altered conformation of FLNA
include PrP , a prion receptor, which Aβ binds at 50- does not appear to promote self-aggregation.
C
100 nmol/L to suppress LTP in slice cultures [37] . Acting
c
as a co-receptor for the Aβ-PrP complex, mGluR5 Best known for cross-linking actin to enable cell
also plays a role in the impaired LTP [38] . Soluble Aβ structure, flexibility and motility, FLNA is a prominent
has also been shown to bind neuroligin-1, a post- regulator of the actin cytoskeletal assembly and
synaptic cell adhesion protein, in the nanomolar range, dynamics [44-46] . The actin cytoskeleton, a vital
and this interaction has been proposed to promote Aβ component in synapses and the dendritic network,
oligomer formation [39] . is impaired in AD [47] . Hence, the FLNA proteopathy
might also disrupt synaptic and dendritic function
Evidence that phosphorylation can alter tau’s in AD by disrupting actin dynamics. FLNA exists
conformation comes from a study showing that a as an intracellular homodimer and dimerizesin a
particular AD-specific phosphorylated tau species membrane-bound, C-terminal domain. It is a large
is only formed when specific phosphoepitopes in a (280-kDa) protein with 24 immunoglobulin repeats
proline-rich region are sequentially phosphorylated by that are natively β-sheet pleated, forming two rod-like
GSK-3β (at Thr212) and then by PKA (at Ser214) [40] . domains separated by two hinge regions. The nature
Whether tau’s hyperphosporylation contributes of the conformational change of FLNA in AD is not
to protein misfolding prior to formation of PHFs is yet known, thoughit is interesting that native FLNA is
speculative, particularly as its pathological structure predominantly β-sheeted. Demonstrating induction by
Neuroimmunology and Neuroinflammation ¦ Volume 4 ¦ December 8, 2017 265