Page 267 - Read Online
P. 267
Burns et al. Altered filamin A enables Aβ signaling
to propagate dysfunction in AD brains.
REVERSING FLNA’S ALTERED
CONFORMATION
The primary evidence for the role of FLNA’s altered
conformation in Aβ 42 ’s toxic signaling via α7nAChR
and TLR4 comes from the small molecule therapeutic
candidate PTI-125. The altered conformation of
FLNA was first inferred from the efficacy (as well as
safety) at relatively low doses of PTI-125 in mouse
models and in vitro, despite a ubiquitous target.
We subsequently determined that PTI-125 binds
altered FLNA (in AD postmortem brain, in 3xTg AD
mice or in ICV Aβ 42 -infused mice) much more tightly
than native FLNA (in control postmortem brain or in
control mice): a femtomolar affinity was measured
for altered FLNA vs. a substantially lower, picomolar
affinity for native FLNA [13] . Using the same isoelectric
focusing point assessment that demonstrated FLNA’s
altered conformation, we further showed that PTI-
125 binding, by in vivo treatment of mice or by in
vitro incubation of postmortem AD brain, restores
N N [13]
the native conformation of FLNA . By reversing the
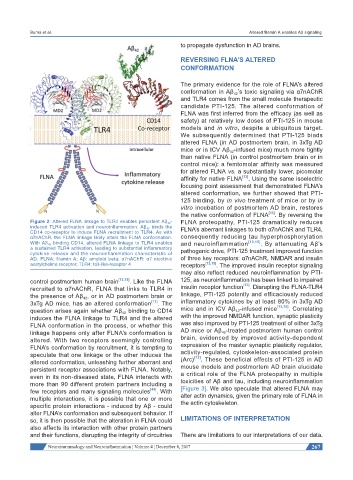
Figure 2: Altered FLNA linkage to TLR4 enables persistent Aβ 42 - FLNA proteopathy, PTI-125 dramatically reduces
induced TLR4 activation and neuroinflammation. Aβ 42 binds the FLNA’s aberrant linkages to both α7nAChR and TLR4,
CD14 co-receptor to induce FLNA recruitment to TLR4. As with
α7nAChR, the FLNA linkage likely alters the FLNA conformation. consequently reducing tau hyperphosphorylation
With Aβ 42 binding CD14, altered FLNA linkage to TLR4 enables and neuroinflammation [13,15] . By attenuating Aβ’s
a sustained TLR4 activation, leading to substantial inflammatory pathogenic drive, PTI-125 treatment improved function
cytokine release and the neuroinflammation characteristic of
AD. FLNA: filamin A; Aβ: amyloid beta; α7nAChR: α7 nicotinic of three key receptors: α7nAChR, NMDAR and insulin
acetylcholine receptor; TLR4: toll-like-receptor 4 receptors [13,15] . The improved insulin receptor signaling
may also reflect reduced neuroinflammation by PTI-
control postmortem human brain [13,15] . Like the FLNA 125, as neuroinflammation has been linked to impaired
recruited to α7nAChR, FLNA that links to TLR4 in insulin receptor function [57] . Disrupting the FLNA-TLR4
the presence of Aβ 42 , or in AD postmortem brain or linkage, PTI-125 potently and efficaciously reduced
3xTg AD mice, has an altered conformation [13] . The inflammatory cytokines by at least 80% in 3xTg AD
[13,15]
question arises again whether Aβ 42 binding to CD14 mice and in ICV Aβ 42 -infused mice . Correlating
induces the FLNA linkage to TLR4 and the altered with the improved NMDAR function, synaptic plasticity
FLNA conformation in the process, or whether this was also improved by PTI-125 treatment of either 3xTg
linkage happens only after FLNA’s conformation is AD mice or Aβ 42 -treated postmortem human control
altered. With two receptors seemingly controlling brain, evidenced by improved activity-dependent
FLNA’s conformation by recruitment, it is tempting to expression of the master synaptic plasticity regulator,
speculate that one linkage or the other induces the activity-regulated, cytoskeleton-associated protein
[13]
altered conformation, unleashing further aberrant and (Arc) . These beneficial effects of PTI-125 in AD
persistent receptor associations with FLNA. Notably, mouse models and postmortem AD brain elucidate
even in its non-diseased state, FLNA interacts with a critical role of the FLNA proteopathy in multiple
more than 90 different protein partners including a toxicities of Aβ and tau, including neuroinflammation
few receptors and many signaling molecules [44] . With [Figure 3]. We also speculate that altered FLNA may
multiple interactions, it is possible that one or more alter actin dynamics, given the primary role of FLNA in
specific protein interactions - induced by Aβ - could the actin cytoskeleton.
alter FLNA’s conformation and subsequent behavior. If
so, it is then possible that the alteration in FLNA could LIMITATIONS OF INTERPRETATION
also affects its interaction with other protein partners
and their functions, disrupting the integrity of circuitries There are limitations to our interpretations of our data.
Neuroimmunology and Neuroinflammation ¦ Volume 4 ¦ December 8, 2017 267