Page 168 - Read Online
P. 168
HIV was negative, the hepatitis B surface antibody, antigen, alpha fetal protein, and carbohydrate antigens
hepatitis B core antibody, hepatitis B e antibody (CA‑199, CA‑125) in the blood. Only CA‑199 was
were all positive. Lung computed tomography (CT) moderately elevated (90.1 U/mL). B‑mode ultrasound
scans showed nodules and fibrous stripes in the scans of the abdomen revealed multiple low signals
right middle lobe, left apex, and lingular lobe, with in the hepatic hilar region and splenic hilum region.
multiple enlarged lymph nodes in the mediastinum. We Ultrasound doctor considered them as enlarged lymph
repeated a lumbar puncture on November 16 , 2009. nodes. CT intensified scans of the upper abdomen
th
The CSF tests showed: pressure 204 mmH O, white showed an occupied lesion in the right hepatic lobe
2
6/
blood cell count 36 × 10 L, protein 0.48 g/L, glucose with intra‑hepatic bile duct dilation. Radiologists
2.70 mmol/L, and chloride 117 mmol/L. The CSF thought the occupied lesion was cholangiocarcinoma,
cytology showed that lymphocytes increased mainly. combining with the history we thought it was
Both acid‑fast staining and the antigen of the tubercle apt to inflammatory pseudotumor, but could not
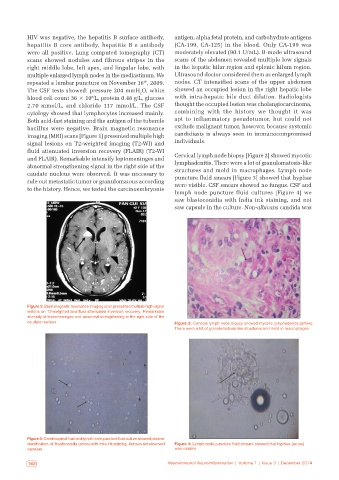
bacillus were negative. Brain magnetic resonance exclude malignant tumor, however, because systemic
imaging (MRI) scans [Figure 1] presented multiple high candidiasis is always seen in immunocompromised
signal lesions on T2‑weighted imaging (T2‑WI) and individuals.
fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) (T2‑WI
and FLAIR). Remarkable intensify leptomeninges and Cervical lymph node biopsy [Figure 2] showed mycotic
abnormal strengthening signal in the right side of the lymphadenitis. There were a lot of granulomatosis‑like
caudate nucleus were observed. It was necessary to structures and mold in macrophages. Lymph node
rule out metastatic tumor or granulomatous according puncture fluid smears [Figure 3] showed that hyphae
were visible. CSF smears showed no fungus. CSF and
to the history. Hence, we tested the carcinoembryonie
lymph node puncture fluid cultures [Figure 4] we
saw blastoconidia with India ink staining, and not
saw capsule in the culture. Non‑albicans candida was
Figure 1: Brain magnetic resonance imaging scan presented multiple high‑signal
lesions on T2-weighted and fluid attenuated inversion recovery. Remarkable
intensity of leptomeninges and abnormal strengthening in the right side of the
caudate nucleus Figure 2: Cervical lymph node biopsy showed mycotic lymphadenitis (arrow).
There were a lot of granulomatosis‑like structures and mold in macrophages
Figure 3: Cerebrospinal fluid and lymph node puncture fluid culture showed positive
identification of blastoconidia (arrow) with India ink staining, but was not observed Figure 4: Lymph node puncture fluid smears showed that hyphae (arrow)
capsules was visiable
162 Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 1 | Issue 3 | December 2014