Page 114 - Read Online
P. 114
tumor cells, in order to detect tumors and validate the are proven to be multifocal gliomas. [29,30] In such
treatment response [Table 1]. cases, FDG PET may aid in pinpointing the area of
stereotactic biopsy, [31,32] assist in tumor delineation
Hypometabolism on FDG PET in brain lesions and during radiotherapy planning [33] and assessment of
stability over a period is indicative of nonmalignancy. treatment response. [34]
[24]
When it is difficult to differentiate preoperatively a
primary brain tumor from metastasis, [25] FDG PET may In a study of 81 recurrent glioma patients studied
be helpful in depicting areas of systemic involvement, by FDG PET, it was found that the higher the FDG
[26]
or localizing the primary cancer site. [27,28] Occasionally, uptake by the tumor it was associated with worse
patients may present with brain lesions, radiologically survival. [35] In addition, pretreatment uptake of FDG
compatible with brain metastases that after biopsy in 25 patients with recurrent gliomas subsequently
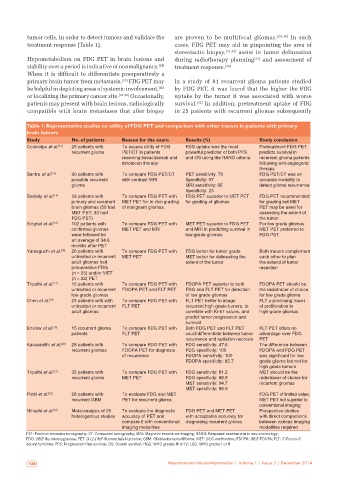
Table 1: Representative studies on utility of FDG PET and comparison with other tracers in patients with primary
brain tumors
Study No. of patients Reason for the exam Results (%) Study conclusion
Colavolpe et al. [12] 25 patients with To assess utility of FDG FDG uptake was the most Pretreatment FDG PET
recurrent glioma PET/CT in patients powerful predictor of both PFS predicts survival in
receiving bevacizumab and and OS using the RANO criteria recurrent glioma patients
irinotecan therapy following anti-angiogenic
therapy
Santra et al. [13] 90 patients with To compare FDG PET/CT PET sensitivity: 70 FDG PET/CT was an
possible recurrent with contrast MRI Specificity: 97 accurate modality to
glioma MRI sensitivity: 95 detect glioma recurrence
Specificity: 23
Borbely et al. [14] 59 patients with To compare FDG PET with FDG PET superior to MET PET FDG PET recommended
primary and recurrent MET PET for in vivo grading for grading of gliomas for grading but MET
brain gliomas (50 had of malignant gliomas PET may be used for
MET PET; 33 had assessing the extent of
FDG PET) the tumor
Singhal et al. [15] 102 patients with To compare FDG PET with MET PET superior to FDG PET For low grade gliomas
confirmed gliomas MET PET and MRI and MRI in predicting survival in MET PET preferred to
were followed for low-grade gliomas FDG PET
an average of 34.6
months after PET
Yamaguchi et al. [16] 26 patients with To compare FDG PET with FDG better for tumor grade Both tracers complement
untreated or recurrent MET PET MET better for delineating the each other to plan
adult gliomas had extent of the tumor the extend of tumor
preoperative FDG resection
(n = 25) and/or MET
(n = 22) PET
Tripathi et al. [17] 15 patients with To compare FDG PET with FDOPA PET superior to both FDOPA PET should be
untreated or recurrent FDOPA PET and FLT PET FDG and FLT PET for detection the radiotracer of choice
low grade gliomas of low grade gliomas for low grade glioma
Chen et al. [18] 25 patients with with To compare FDG PET with FLT PET better to image FLT a promising tracer
untreated or recurrent FLT PET recurrent high-grade tumors, to of proliferation in
adult gliomas correlate with Ki-67 values, and high-grade gliomas
predict tumor progression and
survival
Enslow et al. [19] 15 recurrent glioma To compare FDG PET with Both FDG PET and FLT PET FLT PET offers no
patients FLT PET could differentiate between tumor advantage over FDG
recurrence and radiation necrosis PET
Karunanithi et al. [20] 28 patients with To compare FDG PET with FDG sensitivity: 47.6 The difference between
recurrent gliomas FDOPA PET for diagnosis FDG specificity: 100 FDOPA and FDG PET
of recurrence FDOPA sensitivity: 100 was significant for low
FDOPA specificity: 85.7 grade glioma but not for
high grade tumors
Tripathi et al. [21] 35 patients with To compare FDG PET with FDG sensitivity: 81.2 MET should be the
recurrent glioma MET PET FDG specificity: 88.9 radiotracer of choice for
MET sensitivity: 94.7 recurrent gliomas
MET specificity: 88.9
Potzi et al. [22] 28 patients with To evaluate FDG and MET FDG PET of limited value;
recurrent GBM PET for recurrent glioma MET PET not superior to
conventional imaging
Nihashi et al. [23] Meta-analysis of 26 To evaluate the diagnostic FDG PET and MET PET Prospective studies
heterogenous studies accuracy of PET and with acceptable accuracy for with direct comparisons
compare it with conventional diagnosing recurrent glioma between various imaging
imaging modalities modalities required
PET: Positron emission tomography; CT: Computed tomography; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; RANO: Response assessment in neuro-oncology;
FDG: (18)F-flurodeoxyglucose; FET: O-(2-(18)F-fluoroethyl)-l-tyrosine; GBM: Glioblastomamultiforme; MET: (11)C-methionine; FDOPA: (18)F-FDOPA; FLT: 3’-Fluoro-3’
deoxythymidine; PFS: Progression-free survival; OS: Overall survival; HGG: WHO grades III or IV; LGG: WHO grades I or II
108 Neuroimmunol Neuroinflammation | Volume 1 | Issue 3 | December 2014