Page 125 - Read Online
P. 125
Pham et al. Microbiome Res Rep 2024;3:25 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/mrr.2024.01 Page 13 of 16
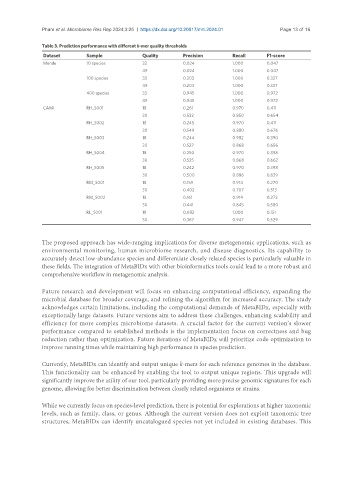
Table 3. Prediction performance with different k-mer quality thresholds
Dataset Sample Quality Precision Recall F1-score
Mende 10 species 33 0.024 1.000 0.047
49 0.024 1.000 0.047
100 species 33 0.203 1.000 0.337
49 0.203 1.000 0.337
400 species 33 0.945 1.000 0.972
49 0.945 1.000 0.972
CAMI RH_S001 18 0.261 0.970 0.411
30 0.532 0.850 0.654
RH_S002 18 0.245 0.970 0.411
30 0.549 0.880 0.676
RH_S003 18 0.244 0.982 0.390
30 0.527 0.868 0.656
RH_S004 18 0.250 0.970 0.398
30 0.535 0.868 0.662
RH_S005 18 0.242 0.970 0.398
30 0.500 0.886 0.639
RM_S001 18 0.159 0.914 0.270
30 0.402 0.707 0.513
RM_S002 18 0.161 0.914 0.273
30 0.441 0.845 0.580
RL_S001 18 0.082 1.000 0.151
30 0.367 0.947 0.529
The proposed approach has wide-ranging implications for diverse metagenomic applications, such as
environmental monitoring, human microbiome research, and disease diagnostics. Its capability to
accurately detect low-abundance species and differentiate closely related species is particularly valuable in
these fields. The integration of MetaBIDx with other bioinformatics tools could lead to a more robust and
comprehensive workflow in metagenomic analysis.
Future research and development will focus on enhancing computational efficiency, expanding the
microbial database for broader coverage, and refining the algorithm for increased accuracy. The study
acknowledges certain limitations, including the computational demands of MetaBIDx, especially with
exceptionally large datasets. Future versions aim to address these challenges, enhancing scalability and
efficiency for more complex microbiome datasets. A crucial factor for the current version’s slower
performance compared to established methods is the implementation focus on correctness and bug
reduction rather than optimization. Future iterations of MetaBIDx will prioritize code optimization to
improve running times while maintaining high performance in species prediction.
Currently, MetaBIDx can identify and output unique k-mers for each reference genomes in the database.
This functionality can be enhanced by enabling the tool to output unique regions. This upgrade will
significantly improve the utility of our tool, particularly providing more precise genomic signatures for each
genome, allowing for better discrimination between closely related organisms or strains.
While we currently focus on species-level prediction, there is potential for explorations at higher taxonomic
levels, such as family, class, or genus. Although the current version does not exploit taxonomic tree
structures, MetaBIDx can identify uncatalogued species not yet included in existing databases. This