Page 615 - Read Online
P. 615
De Iaco et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:63 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.37 Page 9 of 16
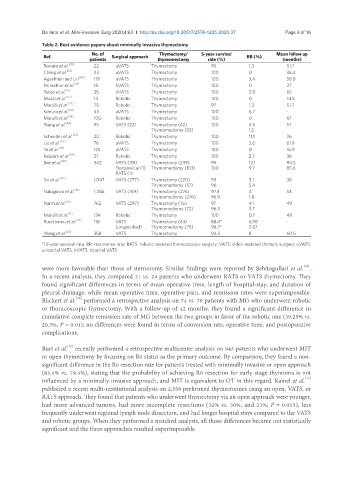
Table 2. Best evidence papers about minimally invasive thymectomy
Ref. No. of Surgical approach Thymectomy/ 5-year survival RR (%) Mean follow up
patients thymomectomy rate (%) (months)
Roviaro et al. [59] 22 uVATS Thymectomy 95 1.3 51.7
Cheng et al. [21] 44 uVATS Thymectomy 100 0 36.4
Agasthian and Lin [60] 119 uVATS Thymectomy 100 3.4 58.8
Pennathur et al. [61] 18 bVATS Thymectomy 100 0 27
Takeo et al. [51] 35 bVATS Thymectomy 100 2.8 65
Mussi et al. [62] 14 Robotic Thymectomy 100 0 14.5
Marulli et al. [22] 79 Robotic Thymectomy 97 1.3 51.7
Kimura et al. [23] 45 uVATS Thymectomy 100 6.7 -
Marulli et al. [54] 100 Robotic Thymectomy 100 0 67
Tseng et al. [83] 95 VATS (22) Thymectomy (42) 100 4.5 57
Thymomectomy (53) 1,5
Schneiter et al. [63] 20 Robotic Thymectomy 100 11.1 26
Liu et al. [64] 76 uVATS Thymectomy 100 2.6 61.9
Ye et al. [65] 125 uVATS Thymectomy 100 0 16.9
Keijzers et al. [66] 37 Robotic Thymectomy 100 2.7 36
Bae et al. [82] 342 VATS (119) Thymectomy (239) 99 12.1 94.5
Transervical (1) Thymomectomy (103) 100 9.7 85.6
RATS (1)
Gu et al. [80] 1,047 VATS (277) Thymectomy (220) 93 3.1 38
Thymomectomy (57) 96 5.4
Nakagawa et al. [81] 1,286 VATS (169) Thymectomy (276) 97.3 4 53
Thymomectomy (276) 96.9 1.8
Narm et al. [79] 762 VATS (297) Thymectomy (76) 97 4.1 49
Thymomectomy (72) 96.3 3.7
Marulli et al. [11] 134 Robotic Thymectomy 100 0.7 48
Rusidanmu et al. [77] 118 VATS Thymectomy (43) 88.4* 6.98 -
(unspecified) Thymomectomy (75) 98.7* 2.67
Weng et al. [67] 358 VATS Thymectomy 94.5 8 60.5
*10-year survival rate. RR: recurrence rate; RATS: robotic-assisted thoracoscopic surgery; VATS: video-assisted thoracic surgery; uVATS:
uniportal VATS; bVATS: biportal VATS
[69]
were more favorable than those of sternotomy. Similar findings were reported by Şehitogullari et al. .
In a recent analysis, they compared 21 vs. 24 patients who underwent RATS or VATS thymectomy. They
found significant differences in terms of mean operative time, length of hospital-stay, and duration of
pleural drainage, while mean operative time, operative pain, and remission rates were superimposable.
[70]
Rückert et al. performed a retrospective analysis on 74 vs. 79 patients with MG who underwent robotic
or thoracoscopic thymectomy. With a follow-up of 42 months, they found a significant difference in
cumulative complete remission rate of MG between the two groups in favor of the robotic one (39.25% vs.
20.3%, P = 0.01); no differences were found in terms of conversion rate, operative time, and postoperative
complications.
[71]
Burt et al. recently performed a retrospective multicenter analysis on 943 patients who underwent MIT
or open thymectomy by focusing on R0 status as the primary outcome. By comparison, they found a non-
significant difference in the R0 resection rate for patients treated with minimally invasive or open approach
(83.4% vs. 79.4%), stating that the probability of achieving R0 resection for early-stage thymoma is not
[72]
influenced by a minimally invasive approach, and MIT is equivalent to OT in this regard. Kamel et al.
published a recent multi-institutional analysis on 2,558 performed thymectomies using an open, VATS, or
RATS approach. They found that patients who underwent thymectomy via an open approach were younger,
had more advanced tumors, had more incomplete resections (32% vs. 30%, and 23%; P = 0.013), less
frequently underwent regional lymph node dissection, and had longer hospital stays compared to the VATS
and robotic groups. When they performed a matched analysis, all those differences became not statistically
significant and the three approaches resulted superimposable.