Page 610 - Read Online
P. 610
Page 4 of 16 De Iaco et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:63 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.37
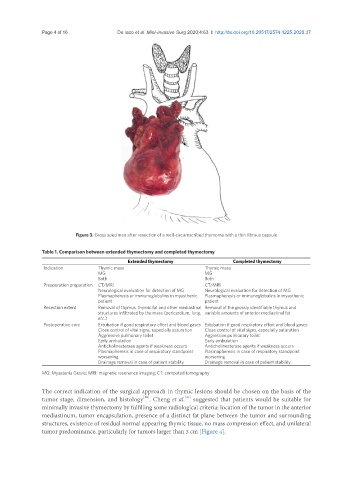
Figure 3. Gross specimen after resection of a well-circumscribed thymoma with a thin fibrous capsule
Table 1. Comparison between extended thymectomy and completed thymectomy
Extended thymectomy Completed thymectomy
Indication Thymic mass Thymic mass
MG MG
Both Both
Preoperation preparation CT/MRI CT/MRI
Neurological evaluation for detection of MG Neurological evaluation for detection of MG
Plasmapheresis or immunoglobulins in myasthenic Plasmapheresis or immunoglobulins in myasthenic
patient patient
Resection extent Removal of thymus, thymic fat and other mediastinal Removal of the grossly identifiable thymus and
structures infiltrated by the mass (pericardium, lung, variable amounts of anterior mediastinal fat
etc.)
Postoperative care Extubation if good respiratory effort and blood gases Extubation if good respiratory effort and blood gases
Close control of vital signs, especially saturation Close control of vital signs, especially saturation
Aggressive pulmonary toilet Aggressive pulmonary toilet
Early ambulation Early ambulation
Anticholinesterase agents if weakness occurs Anticholinesterase agents if weakness occurs
Plasmapheresis in case of respiratory standpoint Plasmapheresis in case of respiratory standpoint
worsening worsening
Drainage removal in case of patient stability Drainage removal in case of patient stability
MG: Myastenia Gravis; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; CT: computed tomography
The correct indication of the surgical approach in thymic lesions should be chosen on the basis of the
tumor stage, dimension, and histology . Cheng et al. suggested that patients would be suitable for
[21]
[20]
minimally invasive thymectomy by fulfilling some radiological criteria: location of the tumor in the anterior
mediastinum, tumor encapsulation, presence of a distinct fat plane between the tumor and surrounding
structures, existence of residual normal appearing thymic tissue, no mass compression effect, and unilateral
tumor predominance, particularly for tumors larger than 3 cm [Figure 4].