Page 53 - Read Online
P. 53
Page 4 of 6 Kawada et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:7 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2019.44
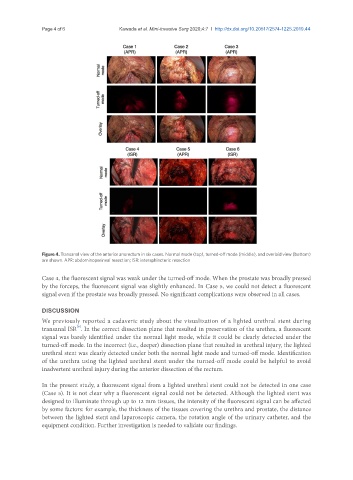
Figure 4. Transanal view of the anterior anorectum in six cases. Normal mode (top), turned-off mode (middle), and overlaid view (bottom)
are shown. APR: abdominoperineal resection; ISR: intersphincteric resection
Case 4, the fluorescent signal was weak under the turned-off mode. When the prostate was broadly pressed
by the forceps, the fluorescent signal was slightly enhanced. In Case 5, we could not detect a fluorescent
signal even if the prostate was broadly pressed. No significant complications were observed in all cases.
DISCUSSION
We previously reported a cadaveric study about the visualization of a lighted urethral stent during
[9]
transanal ISR . In the correct dissection plane that resulted in preservation of the urethra, a fluorescent
signal was barely identified under the normal light mode, while it could be clearly detected under the
turned-off mode. In the incorrect (i.e., deeper) dissection plane that resulted in urethral injury, the lighted
urethral stent was clearly detected under both the normal light mode and turned-off mode. Identification
of the urethra using the lighted urethral stent under the turned-off mode could be helpful to avoid
inadvertent urethral injury during the anterior dissection of the rectum.
In the present study, a fluorescent signal from a lighted urethral stent could not be detected in one case
(Case 5). It is not clear why a fluorescent signal could not be detected. Although the lighted stent was
designed to illuminate through up to 12 mm tissues, the intensity of the fluorescent signal can be affected
by some factors: for example, the thickness of the tissues covering the urethra and prostate, the distance
between the lighted stent and laparoscopic camera, the rotation angle of the urinary catheter, and the
equipment condition. Further investigation is needed to validate our findings.