Page 45 - Read Online
P. 45
Falavolti et al. Early vascular control in robotic surgery
With continued expansions in the field of robotic
surgery, urologists are now available to combine the
advantages of laparoscopic procedures such as shorter
hospitalization, less total amount of blood loss, more
efficient intracorporeal suturing and cosmetic results
and those of robotic surgery: 6 degrees of freedom,
dexterity enhancement, 3-D vision, and tremor filtering.
The feasibility of robotic-assisted adenomectomy was
confirmed by Sotelo et al. in 2008. Their data showed
[7]
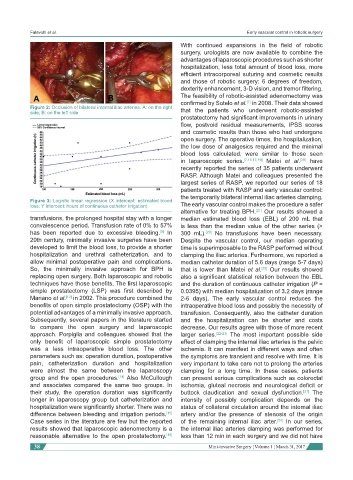
Figure 2: Occlusion of bilateral internal iliac arteries. A: on the right that the patients who underwent robotic-assisted
side; B: on the left side
prostatectomy had significant improvements in urinary
flow, postvoid residual measurements, IPSS scores
and cosmetic results than those who had undergone
open surgery. The operative times, the hospitalization,
the low dose of analgesics required and the minimal
blood loss calculated, were similar to those seen
in laparoscopic series. [7,15,17-19] Matei et al. have
[20]
recently reported the series of 35 patients underwent
RASP. Although Matei and colleagues presented the
largest series of RASP, we reported our series of 18
patients treated with RASP and early vascular control:
the temporarily bilateral internal iliac arteries clamping.
Figure 3: Logistic linear regression (X intercept: estimated blood
loss; Y intercept: hours of continuous catheter irrigation) Theearly vascular control makes the procedure a safer
alternative for treating BPH. Our results showed a
[21]
transfusions, the prolonged hospital stay with a longer median estimated blood loss (EBL) of 200 mL that
convalescence period. Transfusion rate of 0% to 57% is less than the median value of the other series (>
has been reported due to excessive bleeding. In 300 mL). No transfusions have been necessary.
[9]
[20]
20th century, minimally invasive surgeries have been Despite the vascular control, our median operating
developed to limit the blood loss, to provide a shorter time is superimposable to the RASP performed without
hospitalization and urethral catheterization, and to clamping the iliac arteries. Furthermore, we reported a
allow minimal postoperative pain and complications. median catheter duration of 5.6 days (range 5-7 days)
So, the minimally invasive approach for BPH is that is lower than Matei et al. Our results showed
[20]
replacing open surgery. Both laparoscopic and robotic also a significant statistical relation between the EBL
techniques have those benefits. The first laparoscopic and the duration of continuous catheter irrigation (P =
simple prostatectomy (LSP) was first described by 0.0395) with median hospitalization of 3.2 days (range
Mariano et al. in 2002. This procedure combined the 2-6 days). The early vascular control reduces the
[13]
benefits of open simple prostatectomy (OSP) with the intraoperative blood loss and possibly the necessity of
potential advantages of a minimally invasive approach. transfusion. Consequently, also the catheter duration
Subsequently, several papers in the literature started and the hospitalization can be shorter and costs
to compare the open surgery and laparoscopic decrease. Our results agree with those of more recent
approach. Porpiglia and colleagues showed that the larger series. [22-23] The most important possible side
only benefit of laparoscopic simple prostatectomy effect of clamping the internal iliac arteries is the pelvic
was a less intraoperative blood loss. The other ischemia. It can manifest in different ways and often
parameters such as: operation duration, postoperative the symptoms are transient and resolve with time. It is
pain, catheterization duration and hospitalization very important to take care not to prolong the arteries
were almost the same between the laparoscopy clamping for a long time. In these cases, patients
group and the open procedures. Also McCullough can present serious complications such as colorectal
[14]
and associates compared the same two groups. In ischemia, gluteal necrosis and neurological deficit or
their study, the operation duration was significantly buttock claudication and sexual dysfunction. The
[21]
longer in laparoscopy group but catheterization and intensity of possibly complication depends on the
hospitalization were significantly shorter. There was no status of collateral circulation around the internal iliac
difference between bleeding and irrigation periods. artery and/or the presence of stenosis of the origin
[15]
Case series in the literature are few but the reported of the remaining internal iliac arter. In our series,
[24]
results showed that laparoscopic adenomectomy is a the internal iliac arteries clamping was performed for
reasonable alternative to the open prostatectomy. less than 12 min in each surgery and we did not have
[16]
38 Mini-invasive Surgery ¦ Volume 1 ¦ March 31, 2017