Page 84 - Read Online
P. 84
Nakamura et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2022;6:50 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2022.38 Page 5 of 20
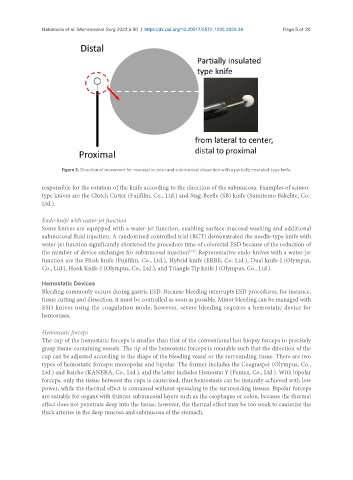
Figure 3. Direction of movement for mucosal incision and submucosal dissection with a partially insulated-type knife.
responsible for the rotation of the knife according to the direction of the submucosa. Examples of scissor-
type knives are the Clutch Cutter (Fujifilm, Co., Ltd.) and Stag-Beetle (SB) knife (Sumitomo Bakelite, Co.,
Ltd.).
Endo-knife with water-jet function
Some knives are equipped with a water-jet function, enabling surface mucosal washing and additional
submucosal fluid injection. A randomized controlled trial (RCT) demonstrated the needle-type knife with
water-jet function significantly shortened the procedure time of colorectal ESD because of the reduction of
the number of device exchanges for submucosal injection . Representative endo-knives with a water-jet
[6,7]
function are the Flush knife (Fujifilm, Co., Ltd.), Hybrid knife (ERBE, Co. Ltd.), Dual knife-J (Olympus,
Co., Ltd.), Hook Knife-J (Olympus, Co., Ltd.), and Triangle Tip knife J (Olympus, Co., Ltd.).
Hemostatic Devices
Bleeding commonly occurs during gastric ESD. Because bleeding interrupts ESD procedures, for instance,
tissue cutting and dissection, it must be controlled as soon as possible. Minor bleeding can be managed with
ESD knives using the coagulation mode; however, severe bleeding requires a hemostatic device for
hemostasis.
Hemostatic forceps
The cup of the hemostatic forceps is smaller than that of the conventional hot biopsy forceps to precisely
grasp tissue-containing vessels. The tip of the hemostatic forceps is rotatable such that the direction of the
cup can be adjusted according to the shape of the bleeding vessel or the surrounding tissue. There are two
types of hemostatic forceps: monopolar and bipolar. The former includes the Coagrasper (Olympus, Co.,
Ltd.) and Raicho (KANEKA, Co., Ltd.), and the latter includes Hemostat Y (Pentax, Co., Ltd.). With bipolar
forceps, only the tissue between the cups is cauterized, thus hemostasis can be instantly achieved with low
power, while the thermal effect is contained without spreading to the surrounding tissues. Bipolar forceps
are suitable for organs with thinner submucosal layers such as the esophagus or colon, because the thermal
effect does not penetrate deep into the tissue; however, the thermal effect may be too weak to cauterize the
thick arteries in the deep mucosa and submucosa of the stomach.