Page 72 - Read Online
P. 72
Page 4 of 11 Suwa et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2022;6:20 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2021.123
Table 1. Evaluation of the risk factors for incompletion of resection
CSP completion CSP incompletion P value
N = 59 N = 5
Location, n
bulb/2nd/3rd 6/51/2 1/4/0
a
bulb/others, n 6/53 1/4 0.46
Endoscopic size, median (range), mm 6 (2-12) 10 (5-10) 0.045 b
Macroscopic type
0-I/0-IIa/0-IIc/0-IIa+IIc 6/47/4/2 1/3/0/1
with 0-IIc component/without 0-IIc, n 6/53 1/4 0.45 a
a
Biopsy before CSP 26/59 (44%) 2/5 (40%) 1.00
Histopathological assessment, n
cancer/adenoma/non-neoplastic 3/46/10 1/4/0
cancer/adenoma + non-neoplastic, n 3/56 1/4 0.28 a
a b
CSP: Cold snare polypectomy. Fisher’s exact test. Mann-Whitney U test.
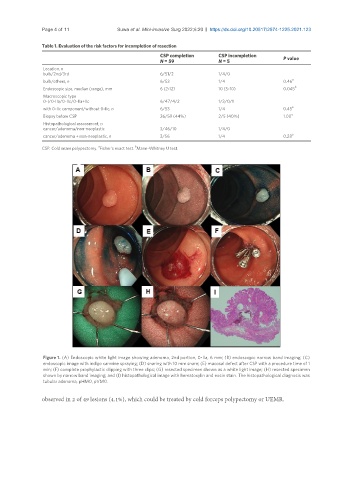
Figure 1. (A) Endoscopic white light image showing adenoma, 2nd portion, 0-IIa, 6 mm; (B) endoscopic narrow band imaging; (C)
endoscopic image with indigo carmine spraying; (D) snaring with 10 mm snare; (E) mucosal defect after CSP with a procedure time of 1
min; (F) complete prophylactic clipping with three clips; (G) resected specimen shown as a white light image; (H) resected specimen
shown by narrow band imaging; and (I) histopathological image with hematoxylin and eosin stain. The histopathological diagnosis was
tubular adenoma, pHM0, pVM0.
observed in 2 of 49 lesions (4.1%), which could be treated by cold forceps polypectomy or UEMR.