Page 40 - Read Online
P. 40
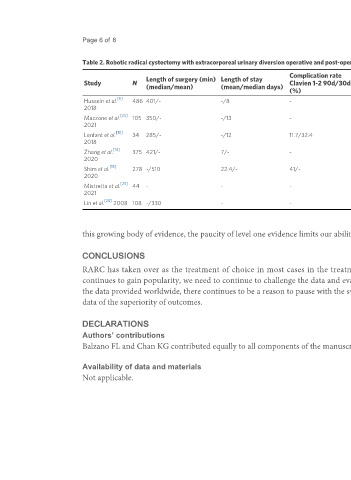
Page 6 of 8 Balzano et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2021;5:41 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2021.49
Table 2. Robotic radical cystectomy with extracorporeal urinary diversion operative and post-operative characteristics
Complication rate Complication rate GI Continence (0-1
Length of surgery (min) Length of stay Overall complication
Study N Clavien 1-2 90d/30d Clavien 3-5 90d/30d complications pad/d) (day %/night
(median/mean) (mean/median days) rate 90d/30d (%)
(%) (%) (%) %)
[5]
Hussein et al. 486 401/- -/8 - 12/10 20 35/28 -
2018
[23]
Mazzone et al. 105 350/- -/13 - -/42.9 - - -
2021
[10]
Lenfant et al. 34 285/- -/12 11.7/32.4 17.6/5.9 - 29.4/38.2 -
2018
[14]
Zhang et al. 375 421/- 7/- - 24.8/17.9 29.3 48.3/43.2 -
2020
[15]
Shim et al. 278 -/510 22.4/- 41/- 20.5/- 12.9 61.5/- -
2020
[25]
Mistretta et al. 44 - - - - - - 63.8/51.6
2021
[28]
Lin et al. 2008 108 -/330 - - - - 18.5 90.7/82.6
this growing body of evidence, the paucity of level one evidence limits our ability to draw definitive conclusions.
CONCLUSIONS
RARC has taken over as the treatment of choice in most cases in the treatment of muscle-invasive bladder cancer. As intracorporeal urinary diversion
continues to gain popularity, we need to continue to challenge the data and evaluate if we are making the right decision for our patients. After looking across
the data provided worldwide, there continues to be a reason to pause with the sweeping adoption of the intracorporeal urinary diversion with continued varied
data of the superiority of outcomes.
DECLARATIONS
Authors’ contributions
Balzano FL and Chan KG contributed equally to all components of the manuscript.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.