Page 39 - Read Online
P. 39
Balzano et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2021;5:41 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2021.49 Page 5 of 8
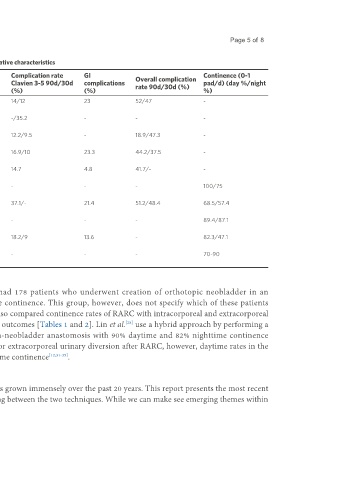
Table 1. Robotic radical cystectomy with intracorporeal urinary diversion operative and post-operative characteristics
Complication rate Complication rate GI Continence (0-1
Length of surgery (min) Length of stay Overall complication
Study N Clavien 1-2 90d/30d Clavien 3-5 90d/30d complications pad/d) (day %/night
(median/mean) (mean/median days) rate 90d/30d (%)
(%) (%) (%) %)
[11]
Hussein et al. 486 355/- -/9 - 14/12 23 52/47 -
2020
[23]
Mazzone et al. 162 350/- -/11.5 - -/35.2 - - -
2021
[10]
Lenfant et al. 74 320/- -/14 6.7/38 12.2/9.5 - 18.9/47.3 -
2018
[14]
Zhang et al. 301 390/- 6/- - 16.9/10 23.3 44.2/37.5 -
2020
[15]
Shim et al. 84 -/566 16.6/- 26.7/- 14.7 4.8 41.7/- -
2020
[24]
Obrecht et al. 12 575/- - - - - - 100/75
2020
[9]
Tyritzis et al. 70 420/- -/9 17/- 37.1/- 21.4 51.2/48.4 68.5/57.4
2013
[25]
Mistretta et al. 57 - - - - - - 89.4/87.1
2021
[26]
Balbay et al. 22 -/552 10.5/- 13.6/92 18.2/9 13.6 - 82.3/47.1
2020
[27]
Tuderti et al. 167 420/- - - - - - 70-90
2020
Grimm et al. , by contrast to the intracorporeal orthotopic neobladder, had 178 patients who underwent creation of orthotopic neobladder in an
[30]
extracorporeal manner with 48.5% daytime continence and 34.9% nighttime continence. This group, however, does not specify which of these patients
underwent RARC as opposed to open radical cystectomy . Mistretta et al. also compared continence rates of RARC with intracorporeal and extracorporeal
[25]
[30]
orthotopic neobladders with no statistically significant difference in functional outcomes [Tables 1 and 2]. Lin et al. use a hybrid approach by performing a
[28]
RARC, extracorporeal creation of the neobladder, and laparoscopic urethra-neobladder anastomosis with 90% daytime and 82% nighttime continence
[Table 2]. Despite this, there is a paucity of data on the functional outcomes for extracorporeal urinary diversion after RARC, however, daytime rates in the
larger open studies range from 54%-99% daytime continence 36%-84.6% nighttime continence [12,31-35] .
Limitations
Overall experience with intracorporeal and extracorporeal urinary diversion has grown immensely over the past 20 years. This report presents the most recent
and robust studies to address the important questions to consider when deciding between the two techniques. While we can make see emerging themes within