Page 42 - Read Online
P. 42
Chandrasekar et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2021;5:33 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2021.12 Page 5 of 16
Table 2. Sensitivity and specificity of various modalities in the diagnosis of malignant biliary strictures
Sensitivity Specificity
ERCP with brush cytology 23%-66% 99%-100%
ERCP with biliary fluid aspiration 6%-36% NA
ERCP with biliary forceps biopsy 45%-81% 99%-100%
Intraductal ultrasound 88%-94% 86%-90%
Endoscopic ultrasound 43%-90% 78%-96%
Spyglass Cholangioscopy 64%-94% 95%-100%
ERCP: Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography.
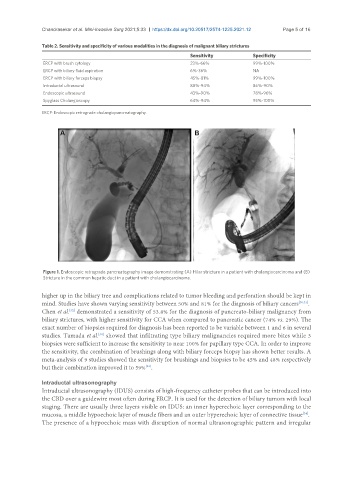
Figure 1. Endoscopic retrograde pancreatography image demonstrating (A) Hilar stricture in a patient with cholangiocarcinoma and (B)
Stricture in the common hepatic duct in a patient with cholangiocarcinoma.
higher up in the biliary tree and complications related to tumor bleeding and perforation should be kept in
mind. Studies have shown varying sensitivity between 50% and 81% for the diagnosis of biliary cancers [30,31] .
[32]
Chen et al. demonstrated a sensitivity of 53.8% for the diagnosis of pancreato-biliary malignancy from
biliary strictures, with higher sensitivity for CCA when compared to pancreatic cancer (74% vs. 29%). The
exact number of biopsies required for diagnosis has been reported to be variable between 1 and 6 in several
studies. Tamada et al. showed that infiltrating type biliary malignancies required more bites while 3
[30]
biopsies were sufficient to increase the sensitivity to near 100% for papillary type CCA. In order to improve
the sensitivity, the combination of brushings along with biliary forceps biopsy has shown better results. A
meta-analysis of 9 studies showed the sensitivity for brushings and biopsies to be 45% and 48% respectively
but their combination improved it to 59% .
[33]
Intraductal ultrasonography
Intraductal ultrasonography (IDUS) consists of high-frequency catheter probes that can be introduced into
the CBD over a guidewire most often during ERCP. It is used for the detection of biliary tumors with local
staging. There are usually three layers visible on IDUS: an inner hyperechoic layer corresponding to the
mucosa, a middle hypoechoic layer of muscle fibers and an outer hyperechoic layer of connective tissue .
[34]
The presence of a hypoechoic mass with disruption of normal ultrasonographic pattern and irregular