Page 11 - Read Online
P. 11
Page 6 of 10 Kauffmann et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:54 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.46
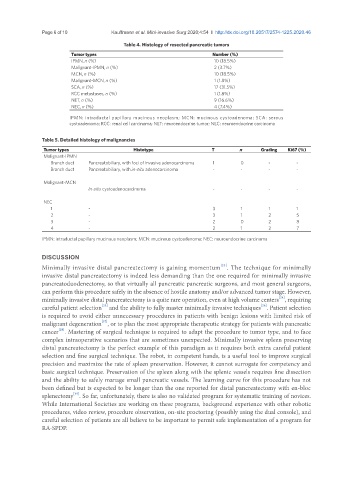
Table 4. Histology of resected pancreatic tumors
Tumor types Number (%)
IPMN, n (%) 10 (18.5%)
Malignant-IPMN, n (%) 2 (3.7%)
MCN, n (%) 10 (18.5%)
Malignant-MCN, n (%) 1 (1.8%)
SCA, n (%) 17 (31.5%)
RCC metastases, n (%) 1 (1.8%)
NET, n (%) 9 (16.6%)
NEC, n (%) 4 (7.4%)
IPMN: intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm; MCN: mucinous cystoadenoma; SCA: serous
cystoadenoma; RCC: renal cell carcinoma; NET: neuroendocrine tumor; NEC: neuroendocrine carcinoma
Table 5. Detailed histology of malignancies
Tumor types Histotype T n Grading Ki67 (%)
Malignant-IPMN
Branch duct Pancreatobiliary, with foci of invasive adenocarcinoma 1 0 - -
Branch duct Pancreatobiliary, with in-situ adenocarcinoma - - - -
Malignant-MCN
In-situ cystoadenocarcinoma - - - -
NEC
1 - 3 1 1 1
2 - 3 1 2 5
3 - 2 0 2 8
4 - 2 1 2 7
IPMN: intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm; MCN: mucinous cystoadenoma; NEC: neuroendocrine carcinoma
DISCUSSION
[23]
Minimally invasive distal pancreatectomy is gaining momentum . The technique for minimally
invasive distal pancreatectomy is indeed less demanding than the one required for minimally invasive
pancreatoduodenectomy, so that virtually all pancreatic pancreatic surgeons, and most general surgeons,
can perform this procedure safely in the absence of hostile anatomy and/or advanced tumor stage. However,
[24]
minimally invasive distal pancreatectomy is a quite rare operation, even at high volume centers , requiring
[25]
careful patient selection and the ability to fully master minimally invasive techniques . Patient selection
[26]
is required to avoid either unnecessary procedures in patients with benign lesions with limited risk of
[27]
malignant degeneration , or to plan the most appropriate therapeutic strategy for patients with pancreatic
[28]
cancer . Mastering of surgical technique is required to adapt the procedure to tumor type, and to face
complex intraoperative scenarios that are sometimes unexpected. Minimally invasive spleen preserving
distal pancreatectomy is the perfect example of this paradigm as it requires both extra careful patient
selection and fine surgical technique. The robot, in competent hands, is a useful tool to improve surgical
precision and maximize the rate of spleen preservation. However, it cannot surrogate for competency and
basic surgical technique. Preservation of the spleen along with the splenic vessels requires fine dissection
and the ability to safely manage small pancreatic vessels. The learning curve for this procedure has not
been defined but is expected to be longer than the one reported for distal pancreatectomy with en-bloc
[15]
splenectomy . So far, unfortunately, there is also no validated program for systematic training of novices.
While International Societies are working on these programs, background experience with other robotic
procedures, video review, procedure observation, on-site proctoring (possibly using the dual console), and
careful selection of patients are all believe to be important to permit safe implementation of a program for
RA-SPDP.