Page 160 - Read Online
P. 160
Sollie et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:80 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.81 Page 5 of 9
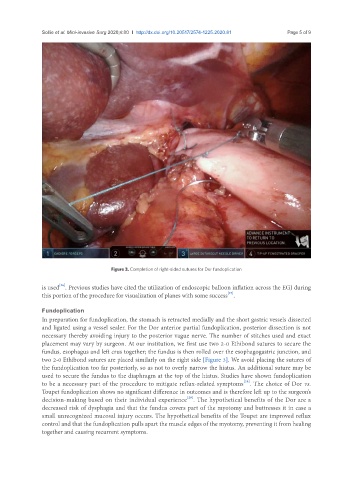
Figure 3. Completion of right-sided sutures for Dor fundoplication
[26]
is used . Previous studies have cited the utilization of endoscopic balloon inflation across the EGJ during
[27]
this portion of the procedure for visualization of planes with some success .
Fundoplication
In preparation for fundoplication, the stomach is retracted medially and the short gastric vessels dissected
and ligated using a vessel sealer. For the Dor anterior partial fundoplication, posterior dissection is not
necessary thereby avoiding injury to the posterior vague nerve. The number of stitches used and exact
placement may vary by surgeon. At our institution, we first use two 2-0 Ethibond sutures to secure the
fundus, esophagus and left crus together; the fundus is then rolled over the esophagogastric junction, and
two 2-0 Ethibond sutures are placed similarly on the right side [Figure 3]. We avoid placing the sutures of
the fundoplication too far posteriorly, so as not to overly narrow the hiatus. An additional suture may be
used to secure the fundus to the diaphragm at the top of the hiatus. Studies have shown fundoplication
[28]
to be a necessary part of the procedure to mitigate reflux-related symptoms . The choice of Dor vs.
Toupet fundoplication shows no significant difference in outcomes and is therefore left up to the surgeon’s
[29]
decision-making based on their individual experience . The hypothetical benefits of the Dor are a
decreased risk of dysphagia and that the fundus covers part of the myotomy and buttresses it in case a
small unrecognized mucosal injury occurs. The hypothetical benefits of the Toupet are improved reflux
control and that the fundoplication pulls apart the muscle edges of the myotomy, preventing it from healing
together and causing recurrent symptoms.