Page 19 - Read Online
P. 19
Ricciardi et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:1 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2019.50 Page 5 of 8
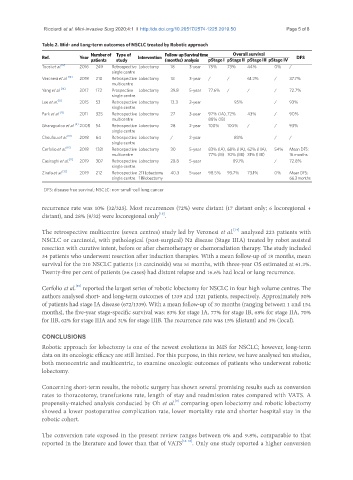
Table 2. Mid- and Long-term outcomes of NSCLC treated by Robotic approach
Number of Type of Follow-up Survival time Overall survival
Ref. Year Intervention DFS
patients study (months) analysis pStage I pStage II pStage III pStage IV
Toosi et al. [6] 2016 249 Retrospective Lobectomy 18 3-year 75% 73% 44% 0% /
single centre
Veronesi et al. [14] 2018 210 Retrospective Lobectomy 18 3-year / / 61.2% / 37.7%
multicentre
Yang et al. [14] 2017 172 Prospective Lobectomy 39.8 5-year 77.6% / / / 72.7%
single centre
Lee et al. [8] 2015 53 Retrospective Lobectomy 13.3 2-year 95% / 93%
single centre
Park et al. [13] 2011 325 Retrospective Lobectomy 27 3-year 97% (IA), 72% 43% / 90%
multicentre 88% (IB)
Gharagozloo et al. [9] 2008 54 Retrospective Lobectomy 28 2-year 100% 100% / / 93%
single centre
Cheufou et al. [10] 2018 64 Retrospective Lobectomy / 2-year 83% / /
single centre
Cerfolio et al. [15] 2018 1321 Retrospective Lobectomy 30 5-year 83% (IA), 68% (IIA), 62% (IIIA), 54% Mean DFS:
multicentre 77% (IB) 70% (IIB) 31% (IIIB) 16 months
Casiraghi et al. [11] 2019 307 Retrospective Lobectomy 28.8 5-year 89.1% / 72.8%
single centre
Zirafa et al. [12] 2019 212 Retrospective 211 Lobectomy 40.3 5-year 98.5% 93.7% 73.1% 0% Mean DFS:
single centre 1 Bilobectomy 66.3 months
DFS: disease free survival; NSCLC: non-small-cell lung cancer
recurrence rate was 10% (32/325). Most recurrences (72%) were distant (17 distant only; 6 locoregional +
[13]
distant), and 28% (9/32) were locoregional only .
[14]
The retrospective multicentre (seven centres) study led by Veronesi et al. analysed 223 patients with
NSCLC or carcinoid, with pathological (post-surgical) N2 disease (Stage IIIA) treated by robot assisted
resection with curative intent, before or after chemotherapy or chemoradiation therapy. The study included
34 patients who underwent resection after induction therapies. With a mean follow-up of 18 months, mean
survival for the 210 NSCLC patients (13 carcinoids) was 51 months, with three-year OS estimated at 61.2%.
Twenty-five per cent of patients (56 cases) had distant relapse and 16.6% had local or lung recurrence.
[15]
Cerfolio et al. reported the largest series of robotic lobectomy for NSCLC in four high volume centres. The
authors analysed short- and long-term outcomes of 1339 and 1321 patients, respectively. Approximately 50%
of patients had stage IA disease (672/1339). With a mean follow-up of 30 months (ranging between 1 and 154
months), the five-year stage-specific survival was: 83% for stage IA, 77% for stage IB, 68% for stage IIA, 70%
for IIB, 62% for stage IIIA and 31% for stage IIIB. The recurrence rate was 15% (distant) and 3% (local).
CONCLUSIONS
Robotic approach for lobectomy is one of the newest evolutions in MIS for NSCLC; however, long-term
data on its oncologic efficacy are still limited. For this purpose, in this review, we have analysed ten studies,
both monocentric and multicentric, to examine oncologic outcomes of patients who underwent robotic
lobectomy.
Concerning short-term results, the robotic surgery has shown several promising results such as conversion
rates to thoracotomy, transfusions rate, length of stay and readmission rates compared with VATS. A
[5]
propensity-matched analysis conducted by Oh et al. comparing open lobectomy and robotic lobectomy
showed a lower postoperative complication rate, lower mortality rate and shorter hospital stay in the
robotic cohort.
The conversion rate exposed in the present review ranges between 0% and 9.8%, comparable to that
reported in the literature and lower than that of VATS [16-18] . Only one study reported a higher conversion