Page 29 - Read Online
P. 29
Cicero et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2019;3:25 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2018.012 Page 7 of 11
A B
C D
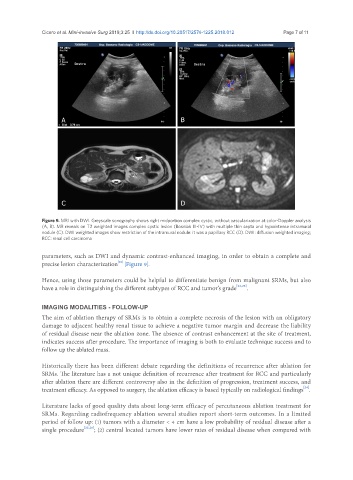
Figure 9. MRI with DWI. Greyscale sonography shows right midportion complex cystic, without vascularization at color-Doppler analysis
(A, B). MR reveals on T2 weighted images complex cystic lesion (Bosniak III-IV) with multiple thin septa and hypointense intramural
nodule (C). DWI weighted images show restriction of the intramural nodule: it was a papillary RCC (D). DWI: diffusion weighted imaging;
RCC: renal cell carcinoma
parameters, such as DWI and dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging, in order to obtain a complete and
[21]
precise lesion characterization [Figure 9].
Hence, using those parameters could be helpful to differentiate benign from malignant SRMs, but also
have a role in distinguishing the different subtypes of RCC and tumor’s grade [22,23] .
IMAGING MODALITIES - FOLLOW-UP
The aim of ablation therapy of SRMs is to obtain a complete necrosis of the lesion with an obligatory
damage to adjacent healthy renal tissue to achieve a negative tumor margin and decrease the liability
of residual disease near the ablation zone. The absence of contrast enhancement at the site of treatment,
indicates success after procedure. The importance of imaging is both to evaluate technique success and to
follow up the ablated mass.
Historically there has been different debate regarding the definitions of recurrence after ablation for
SRMs. The literature has a not unique definition of recurrence after treatment for RCC and particularly
after ablation there are different controversy also in the definition of progression, treatment success, and
treatment efficacy. As opposed to surgery, the ablation efficacy is based typically on radiological findings .
[24]
Literature lacks of good quality data about long-term efficacy of percutaneous ablation treatment for
SRMs. Regarding radiofrequency ablation several studies report short-term outcomes. In a limited
period of follow up: (1) tumors with a diameter < 4 cm have a low probability of residual disease after a
single procedure [25,26] ; (2) central located tumors have lower rates of residual disease when compared with