Page 27 - Read Online
P. 27
Page 6 of 9 Murillo et al. Mini-invasive Surg. 2025;9:7 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2024.55
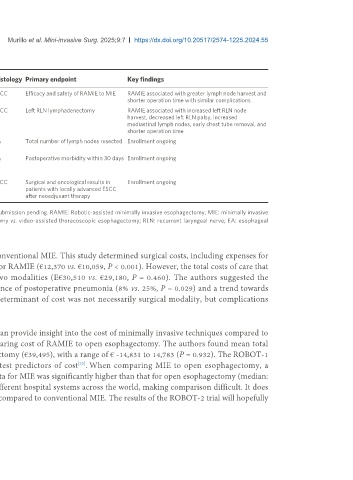
Table 1. Completed and ongoing randomized controlled trials for RAMIE
Study Year Number of Location Surgical procedures Histology Primary endpoint Key findings
name patients
RAMIE 2022 358 China RAMIE ESCC Efficacy and safety of RAMIE to MIE RAMIE associated with greater lymph node harvest and
trial Conventional total MIE shorter operation time with similar complications
REVATE 2022 212 China and RAMIE ESCC Left RLN lymphadenectomy RAMIE associated with increased left RLN node
1
trial Taiwan Conventional total MIE harvest, decreased left RLN palsy, increased
mediastinal lymph nodes, early chest tube removal, and
shorter operation time
ROBOT-2 Ongoing Enrolling Europe RAMIE EA Total number of lymph nodes resected Enrollment ongoing
trial Conventional total MIE
MICkey Ongoing Enrolling Germany and Hybrid esophagectomy (laparoscopic/robotic EA Postoperative morbidity within 30 days Enrollment ongoing
trial the Netherlands abdominal and open thoracic surgery) to total
MIE (robotic/laparoscopic)
RAMIE-2 Ongoing Enrolling China RAMIE ESCC Surgical and oncological results in Enrollment ongoing
Conventional total MIE patients with locally advanced ESCC
after neoadjuvant therapy
1
REVATE trial preliminary results with abstract presented at UGIRA Conference 2024 with manuscript submission pending. RAMIE: Robotic-assisted minimally invasive esophagectomy; MIE: minimally invasive
esophagectomy; ESCC: esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; REVATE: robotic-assisted esophagectomy vs. video-assisted thoracoscopic esophagectomy; RLN: recurrent laryngeal nerve; EA: esophageal
adenocarcinoma.
one single institution study from Germany comparing costs in RAMIE and conventional MIE. This study determined surgical costs, including expenses for
disposable instruments and sterilization of reusable instruments, were higher for RAMIE (€12,370 vs. €10,059, P < 0.001). However, the total costs of care that
includes the postoperative hospitalization were comparable between the two modalities (E€30,510 vs. €29,180, P = 0.460). The authors suggested the
equalization of cost could be attributed to RAMIE resulting in a lower incidence of postoperative pneumonia (8% vs. 25%, P = 0.029) and a trend towards
[32]
shorter hospital stays (15 vs. 17 days, P = 0.205) . Therefore, the greatest determinant of cost was not necessarily surgical modality, but complications
resulting in longer hospital stays.
Though not directly comparing conventional MIE to RAMIE, previous trials can provide insight into the cost of minimally invasive techniques compared to
open esophagectomy. The ROBOT-1 trial published a follow-up study comparing cost of RAMIE to open esophagectomy. The authors found mean total
hospital costs were comparable between RAMIE (€40,211) and open esophagectomy (€39,495), with a range of € -14,831 to 14,783 (P = 0.932). The ROBOT-1
group similarly concluded that postoperative complications were the greatest predictors of cost . When comparing MIE to open esophagectomy, a
[33]
randomized control trial with 5,000 cases found overall treatment cost per capita for MIE was significantly higher than that for open esophagectomy (median:
$9,600 vs. $8,200, P < 0.001) . Notably, these studies were all completed in different hospital systems across the world, making comparison difficult. It does
[34]
not appear at this time that RAMIE has significantly different total cost of care compared to conventional MIE. The results of the ROBOT-2 trial will hopefully