Page 49 - Read Online
P. 49
Page 6 of 11 Sullivan et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2023;7:15 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2022.106
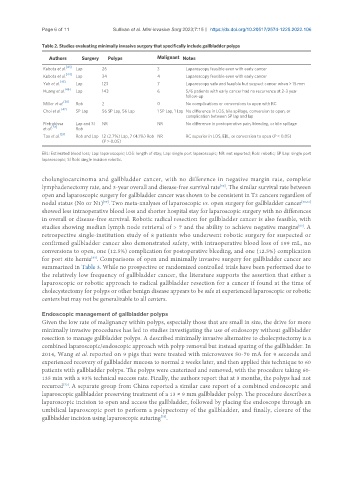
Table 2. Studies evaluating minimally invasive surgery that specifically include gallbladder polyps
Authors Surgery Polyps Malignant Notes
[43]
Kubota et al. Lap 26 3 Laparoscopy feasible even with early cancer
Kubota et al. [44] Lap 34 4 Laparoscopy feasible even with early cancer
[45]
Yeh et al. Lap 123 7 Laparoscopy safe and feasible but suspect cancer when > 15 mm
Huang et al. [46] Lap 143 6 5/6 patients with early cancer had no recurrence at 2-3 year
follow-up
[50]
Miller et al. Rob 2 0 No complications or conversions to open with RC
Choi et al. [47] SP Lap 56 SP Lap, 56 Lap 1 SP Lap, 1 Lap No difference in LOS, bile spillage, conversion to open, or
complication between SP lap and lap
Pietrabissa Lap and SI NR NR No difference in postoperative pain, bleeding, or bile spillage
[54]
et al. Rob
Tao et al. [53] Rob and Lap 12 (2.7%) Lap, 7 (4.1%) Rob NR RC superior in LOS, EBL, or conversion to open (P < 0.05)
(P > 0.05)
EBL: Estimated blood loss; Lap: laparoscopic; LOS: length of stay; Lap: single port laparoscopic; NR: not reported; Rob: robotic; SP Lap: single port
laparoscopic; SI Rob: single incision robotic.
cholangiocarcinoma and gallbladder cancer, with no difference in negative margin rate, complete
[58]
lymphadenectomy rate, and 3-year overall and disease-free survival rate . The similar survival rate between
open and laparoscopic surgery for gallbladder cancer was shown to be consistent in T2 cancers regardless of
nodal status (N0 or N1) . Two meta-analyses of laparoscopic vs. open surgery for gallbladder cancer [60,61]
[59]
showed less intraoperative blood loss and shorter hospital stay for laparoscopic surgery with no differences
in overall or disease-free survival. Robotic radical resection for gallbladder cancer is also feasible, with
studies showing median lymph node retrieval of > 7 and the ability to achieve negative margins . A
[62]
retrospective single-institution study of 8 patients who underwent robotic surgery for suspected or
confirmed gallbladder cancer also demonstrated safety, with intraoperative blood loss of 199 mL, no
conversions to open, one (12.5%) complication for postoperative bleeding, and one (12.5%) complication
for port site hernia . Comparisons of open and minimally invasive surgery for gallbladder cancer are
[63]
summarized in Table 3. While no prospective or randomized controlled trials have been performed due to
the relatively low frequency of gallbladder cancer, the literature supports the assertion that either a
laparoscopic or robotic approach to radical gallbladder resection for a cancer if found at the time of
cholecystectomy for polyps or other benign disease appears to be safe at experienced laparoscopic or robotic
centers but may not be generalizable to all centers.
Endoscopic management of gallbladder polyps
Given the low rate of malignancy within polyps, especially those that are small in size, the drive for more
minimally invasive procedures has led to studies investigating the use of endoscopy without gallbladder
resection to manage gallbladder polyps. A described minimally invasive alternative to cholecystectomy is a
combined laparoscopic/endoscopic approach with polyp removal but instead sparing of the gallbladder. In
2014, Wang et al. reported on 9 pigs that were treated with microwaves 50-70 mA for 9 seconds and
experienced recovery of gallbladder mucosa to normal 2 weeks later, and then applied this technique to 60
patients with gallbladder polyps. The polyps were cauterized and removed, with the procedure taking 60-
135 min with a 93% technical success rate. Finally, the authors report that at 3 months, the polyps had not
recurred . A separate group from China reported a similar case report of a combined endoscopic and
[72]
laparoscopic gallbladder preserving treatment of a 13 × 9 mm gallbladder polyp. The procedure describes a
laparoscopic incision to open and access the gallbladder, followed by placing the endoscope through an
umbilical laparoscopic port to perform a polypectomy of the gallbladder, and finally, closure of the
gallbladder incision using laparoscopic suturing .
[73]