Page 28 - Read Online
P. 28
Adams et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2023;7:18 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2023.12 Page 7 of 12
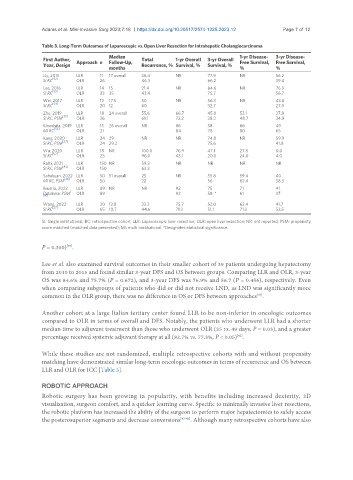
Table 3. Long-Term Outcomes of Laparoscopic vs. Open Liver Resection for Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma
Median 1-yr Disease- 3-yr Disease-
First Author, Approach n Follow-Up, Total 1-yr Overall 3-yr Overall Free Survival, Free Survival,
Year, Design months Recurrence, % Survival, % Survival, % % %
Uy, 2015 LLR 11 17 overall 36.4 NR 77.9 NR 56.2
[52]
SI RC OLR 26 46.3 66.2 39.4
Lee, 2016 LLR 14 15 21.4 NR 84.6 NR 76.9
[53]
SI RC OLR 23 35 43.4 75.7 56.7
Wei, 2017 LLR 12 17.5 50 NR 56.3 NR 43.8
[54]
SI RC OLR 20 12 60 32.7 27.9
Zhu, 2019 LLR 18 24 overall 55.6 66.7 45.8 53.1 37.8
[55]
SI RC, PSM OLR 36 61.1 72.2 38.2 48.7 34.9
Kinoshita, 2019 LLR 15 26 overall NR 86 58 66 49
MI RC [56] OLR 21 84 78 80 65
Kang, 2020 LLR 24 29 NR NR 74.8 NR 59.9
SI RC, PSM [37] OLR 24 29.2 75.6 41.8
Wu, 2020 LLR 18 NR 100.0 76.9 47.1 27.8 0.0
SI RC [57] OLR 25 96.0 43.1 20.0 24.0 4.0
Ratti, 2021 LLR 150 NR 59.3 NR NR NR NR
SI RC, PSM [42] OLR 150 63.3
Sahakyan, 2022 LLR 50 51 overall 25 NR 55.8 59.4 40
MI RC, PSM [28] OLR 50 22 56 62.4 38.3
Brustia, 2022 LLR 89 NR NR 92 75 71 41
[
Database, PSM OLR 89 92 58 * 61 37
59]
Wang, 2022 LLR 30 13.8 33.3 75.7 52.0 63.4 41.7
SI RC [27] OLR 65 10.7 44.6 71.3 51.1 71.3 53.5
SI: Single institutional; RC: retrospective cohort; LLR: Laparoscopic liver resection; OLR: open liver resection; NR: not reported; PSM: propensity
score matched (matched data presented); MI: multi-institutional. *Designates statistical significance.
[37]
P = 0.350) .
Lee et al. also examined survival outcomes in their smaller cohort of 39 patients undergoing hepatectomy
from 2010 to 2015 and found similar 3-year DFS and OS between groups. Comparing LLR and OLR, 3-year
OS was 84.6% and 75.7% (P = 0.672), and 3-year DFS was 76.9% and 56.7 (P = 0.456), respectively. Even
when comparing subgroups of patients who did or did not receive LND, as LND was significantly more
[39]
common in the OLR group, there was no difference in OS or DFS between approaches .
Another cohort at a large Italian tertiary center found LLR to be non-inferior in oncologic outcomes
compared to OLR in terms of overall and DFS. Notably, the patients who underwent LLR had a shorter
median time to adjuvant treatment than those who underwent OLR (35 vs. 49 days, P = 0.03), and a greater
percentage received systemic adjuvant therapy at all (82.7% vs. 77.3%, P < 0.05) .
[42]
While these studies are not randomized, multiple retrospective cohorts with and without propensity
matching have demonstrated similar long-term oncologic outcomes in terms of recurrence and OS between
LLR and OLR for ICC [Table 3].
ROBOTIC APPROACH
Robotic surgery has been growing in popularity, with benefits including increased dexterity, 3D
visualization, surgeon comfort, and a quicker learning curve. Specific to minimally invasive liver resections,
the robotic platform has increased the ability of the surgeon to perform major hepatectomies to safely access
the posterosuperior segments and decrease conversions [43-46] . Although many retrospective cohorts have also