Page 26 - Read Online
P. 26
Adams et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2023;7:18 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2023.12 Page 5 of 12
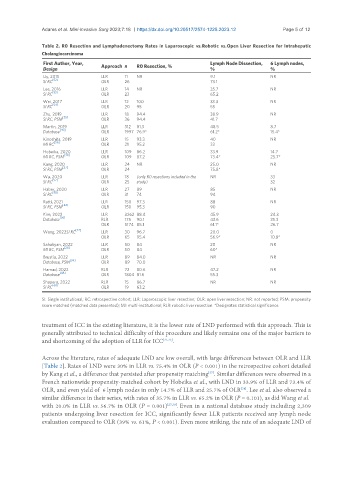
Table 2. R0 Resection and Lymphadenectomy Rates in Laparoscopic vs. Robotic vs. Open Liver Resection for Intrahepatic
Cholangiocarcinoma
First Author, Year, Approach n R0 Resection, % Lymph Node Dissection, 6 Lymph nodes,
Design % %
Uy, 2015 LLR 11 NR 9.1 NR
SI RC [52] OLR 26 73.1
Lee, 2016 LLR 14 NR 35.7 NR
[53]
SI RC OLR 23 65.2
Wei, 2017 LLR 12 100 33.3 NR
SI RC [54] OLR 20 95 55
Zhu, 2019 LLR 18 94.4 38.9 NR
[55]
SI RC, PSM OLR 36 94.4 41.7
Martin, 2019 LLR 312 81.3 48.5 8.7
[40]
Database OLR 1997 76.9* 61.2* 15.4*
Kinoshita, 2019 LLR 15 93.3 40 NR
[56]
MI RC OLR 21 95.2 33
Hobeika, 2020 LLR 109 86.2 33.9 14.7
[38]
MI RC, PSM OLR 109 87.2 73.4* 25.7*
Kang, 2020 LLR 24 NR 25.0 NR
[37]
SI RC, PSM OLR 24 75.8*
Wu, 2020 LLR 18 (only R0 resections included in the NR 33
SI RC [57] OLR 25 study) 32
Haber, 2020 LLR 27 89 85 NR
SI RC [58] OLR 31 74 94
Ratti, 2021 LLR 150 97.3 88 NR
SI RC, PSM [42] OLR 150 95.3 90
Kim, 2022 LLR 3262 88.4 45.9 24.3
Database [36] RLR 175 90.1 43.6 35.3
OLR 5174 85.1 61.1* 26.7
[27]
Wang, 2022SI RC LLR 30 96.7 20.0 0
OLR 65 95.4 56.9* 10.8*
Sahakyan, 2022 LLR 50 84 20 NR
[28]
MI RC, PSM OLR 50 84 60*
Brustia, 2022 LLR 89 84.0 NR NR
Database, PSM [59] OLR 89 70.0
Hamad, 2022 RLR 72 80.6 47.2 NR
Database [48] OLR 1804 81.6 55.3
Shapera, 2022 RLR 15 86.7 NR NR
SI RC [60] OLR 19 63.2
SI: Single institutional; RC: retrospective cohort; LLR: Laparoscopic liver resection; OLR: open liver resection; NR: not reported; PSM: propensity
score matched (matched data presented); MI: multi-institutional; RLR: robotic liver resection. *Designates statistical significance.
treatment of ICC in the existing literature, it is the lower rate of LND performed with this approach. This is
generally attributed to technical difficulty of this procedure and likely remains one of the major barriers to
and shortcoming of the adoption of LLR for ICC [21,22] .
Across the literature, rates of adequate LND are low overall, with large differences between OLR and LLR
[Table 2]. Rates of LND were 30% in LLR vs. 75.4% in OLR (P < 0.001) in the retrospective cohort detailed
by Kang et al., a difference that persisted after propensity matching . Similar differences were observed in a
[37]
French nationwide propensity-matched cohort by Hobeika et al., with LND in 33.9% of LLR and 73.4% of
OLR, and even yield of 6 lymph nodes in only 14.7% of LLR and 25.7% of OLR . Lee et al. also observed a
[38]
similar difference in their series, with rates of 35.7% in LLR vs. 65.2% in OLR (P = 0.101), as did Wang et al.
with 20.0% in LLR vs. 56.7% in OLR (P = 0.001) [27,39] . Even in a national database study including 2,309
patients undergoing liver resection for ICC, significantly fewer LLR patients received any lymph node
evaluation compared to OLR (39% vs. 61%, P < 0.001). Even more striking, the rate of an adequate LND of