Page 55 - Read Online
P. 55
Estévez-Arias et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2022;6:333-52 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2022.04 Page 339
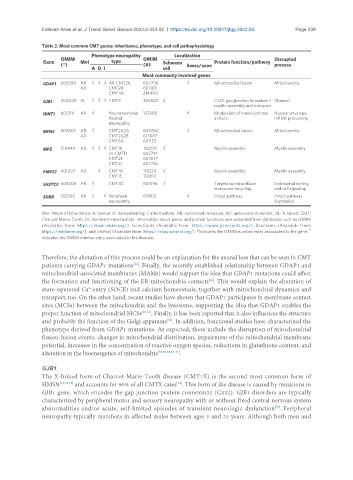
Table 2. Most common CMT genes: inheritance, phenotype, and cell pathophysiology
Phenotype neuropathy Localization
OMIM OMIM Disrupted
Gene MoI type Schwann Protein function/pathway
(*) (#) Soma/axon process
A D I cell
Most commonly involved genes
GDAP1 606598 AR √ √ √ AR-CMT2K 607706 √ Mitochondria fission Mitochondria
AD CMT2K 607831
CMT4A 214400
GJB1 304040 XL √ √ √ CMTX 302800 √ Cx32: gap junction formation + Channel
myelin assembly and transport
HINT1 601314 AR √ Neuromyotonia 137200 √ Modulation of transcriptional Nuclear envelope,
Axonal activity mRNA processing
neuropathy
MFN2 608507 AR √ CMT2A2A 609260 √ Mitochondrial fusion Mitochondria
AD CMT2A2B 617087
CMT6A 601152
MPZ 159440 AD √ √ √ CMT1B 118200 √ Myelin assembly Myelin assembly
DI-CMTD 607791
CMT2I 607677
CMT2J 607736
PMP22 601097 AD √ CMT1A 118220 √ Myelin assembly Myelin assembly
CMT1E 118300
SH3TC2 608206 AR √ CMT4C 601596 √ Targets to intracellular Endosomal sorting
endosome recycling and cell signaling
SORD 182500 AR √ √ Peripheral 618912 √ Polyol pathway Polyol pathway
neuropathy (cytosolic)
MoI: Mode of inheritance; A: axonal; D: demyelinating; I: intermediate; AR: autosomal recessive; AD: autosomal dominant; XL: X-linked; CMT:
Charcot-Marie-Tooth; DI: dominant intermediate. Information about genes and protein functions was extracted from databases such as OMIM
(Available from: https://www.omim.org/), GeneCards (Available from: https://www.genecards.org/), Reactome (Available from:
#
https://reactome.org/), and UniProt (Available from: https://www.uniprot.org/). *indicates the OMIM number entry associated to the gene;
indicates the OMIM number entry associated to the disorder.
Therefore, the alteration of this process could be an explanation for the axonal loss that can be seen in CMT
patients carrying GDAP1 mutations . Finally, the recently established relationship between GDAP1 and
[56]
mitochondrial-associated membranes (MAMs) would support the idea that GDAP1 mutations could affect
[66]
the formation and functioning of the ER-mitochondria contacts . This would explain the alteration of
store-operated Ca entry (SOCE) and calcium homeostasis, together with mitochondrial dynamics and
2+
transport, too. On the other hand, recent studies have shown that GDAP1 participates in membrane contact
sites (MCSs) between the mitochondria and the lysosome, supporting the idea that GDAP1 enables the
proper function of mitochondrial MCSs [62,67] . Finally, it has been reported that it also influences the structure
and probably the function of the Golgi apparatus . In addition, functional studies have characterized the
[59]
phenotype derived from GDAP1 mutations. As expected, these include the disruption of mitochondrial
fission-fusion events, changes in mitochondrial distribution, impairment of the mitochondrial membrane
potential, increases in the concentration of reactive oxygen species, reductions in glutathione content, and
alteration in the bioenergetics of mitochondria [57,64,65,68-71] .
GJB1
The X-linked form of Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease (CMT1X) is the second most common form of
HMSN [13,72,73] and accounts for 90% of all CMTX cases . This form of the disease is caused by mutations in
[74]
GJB1 gene, which encodes the gap junction protein connexin32 (Cx32). GJB1 disorders are typically
characterized by peripheral motor and sensory neuropathy with or without fixed central nervous system
[75]
abnormalities and/or acute, self-limited episodes of transient neurologic dysfunction . Peripheral
neuropathy typically manifests in affected males between ages 5 and 25 years. Although both men and