Page 42 - Read Online
P. 42
Waller et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2021;5:112-23 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2021.09 Page 114
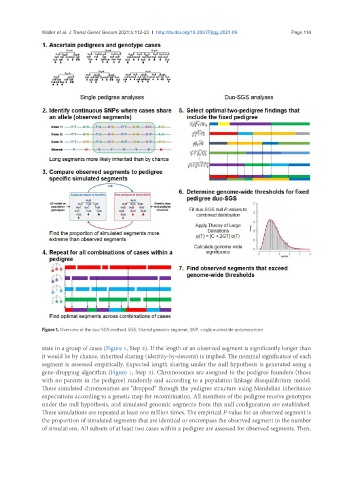
Figure 1. Overview of the duo-SGS method. SGS: Shared genomic segment; SNP: single nucleotide polymorphism.
state in a group of cases (Figure 1, Step 2). If the length of an observed segment is significantly longer than
it would be by chance, inherited sharing (identity-by-descent) is implied. The nominal significance of each
segment is assessed empirically. Expected length sharing under the null hypothesis is generated using a
gene-dropping algorithm (Figure 1, Step 3). Chromosomes are assigned to the pedigree founders (those
with no parents in the pedigree) randomly and according to a population linkage disequilibrium model.
These simulated chromosomes are “dropped” through the pedigree structure using Mendelian inheritance
expectations according to a genetic map for recombination. All members of the pedigree receive genotypes
under the null hypothesis, and simulated genomic segments from this null configuration are established.
These simulations are repeated at least one million times. The empirical P-value for an observed segment is
the proportion of simulated segments that are identical or encompass the observed segment to the number
of simulations. All subsets of at least two cases within a pedigree are assessed for observed segments. Then,