Page 116 - Read Online
P. 116
Jiang et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2021;5:323-40 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2021.21 Page 329
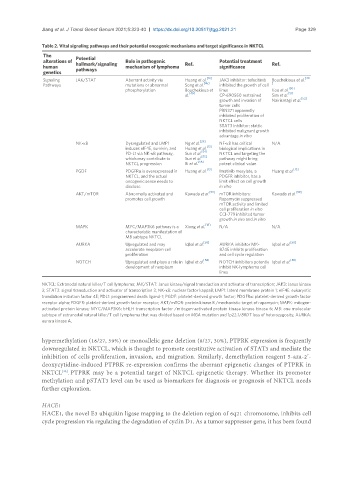
Table 2. Vital signaling pathways and their potential oncogenic mechanisms and target significance in NKTCL
The Potential
alterations of hallmark/signaling Role in pathogenic Ref. Potential treatment Ref.
human pathways mechanism of lymphoma significance
genetics
[13] [49
Signaling JAK/STAT Aberrant activity via Huang et al. JAK3 inhibitor: tofacitinib Bouchekioua et al.
Pathways mutations or abnormal Song et al. [45] inhibited the growth of cell ]
[50]
phosphorylation Bouchekioua et lines Koo et al.
al. [49] CP-690550 restrained Sim et al. [51]
[52]
growth and invasion of Nairismägi et al.
tumor cells
PRN371 apparently
inhibited proliferation of
NKTCL cells
STAT3 inhibitor: stattic
inhibited malignant growth
advantage in vitro
NK-κB Dysregulated and LMP1 Ng et al. [29] NF-κB has critical N/A
[13]
induces eIF4E, survivin, and Huang et al. biological implications in
PD-L1 via NK-κB pathway, Sun et al. [54] NKTCL and targeting the
[55]
which may contribute to Sun et al. pathway might bring
NKTCL progression Bi et al. [56] potent clinical value
[13] [13]
PGDF PDGFRα is overexpressed in Huang et al. Imatinib mesylate, a Huang et al.
NKTCL, and the actual PDGFR inhibitor, has a
oncogenic sense needs to limit effect on cell growth
disclose in vitro
AKT/mTOR Abnormally activated and Kawada et al. [59] mTOR inhibitors: Kawada et al. [59]
promotes cell growth Rapamycin suppressed
mTOR activity and limited
cell proliferation in vitro
CCI-779 inhibited tumor
growth in vivo and in vitro
[18]
MAPK MYC/MAP3K6 pathway is a Xiong et al. N/A N/A
characteristic manifestation of
MB subtype NKTCL
AURKA Upregulated and may Iqbal et al. [58] AURKA inhibitor MK- Iqbal et al. [58]
accelerate neoplasm cell 8745 inhibits proliferation
proliferation and cell cycle regulation
[58] [58]
NOTCH Upregulated and plays a role in Iqbal et al. NOTCH inhibitors potently Iqbal et al.
development of neoplasm inhibit NK-lymphoma cell
lines
NKTCL: Extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma; JAK/STAT: Janus kinase/signal transduction and activator of transcription; JAK3: Janus kinase
3; STAT3: signal transduction and activator of transcription 3; NK-κB: nuclear factor kappaB; LMP1: latent membrane protein 1; eIF4E: eukaryotic
translation initiation factor 4E; PDL1: programmed death ligand-1; PGDF: platelet-derived growth factor; PDGFRα: platelet-derived growth factor
receptor alpha; PDGFR: platelet-derived growth factor receptor; AKT/mTOR: protein kinase B /mechanistic target of rapamycin; MAPK: mitogen-
activated protein kinase; MYC/MAP3K6: bHLH transcription factor /mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 6; MB: one molecular
subtype of extranodal natural killer/T cell lymphoma that was divided based on MGA mutation and 1p22.1/BRDT loss of heterozygosity; AURKA:
aurora kinase A.
hypermethylation (16/27, 59%) or monoallelic gene deletion (8/27, 30%), PTPRK expression is frequently
downregulated in NKTCL, which is thought to promote constitutive activation of STAT3 and mediate the
inhibition of cells proliferation, invasion, and migration. Similarly, demethylation reagent 5-aza-2’-
deoxycytidine-induced PTPRK re-expression confirms the aberrant epigenetic changes of PTPRK in
NKTCL . PTPRK may be a potential target of NKTCL epigenetic therapy. Whether its promoter
[48]
methylation and pSTAT3 level can be used as biomarkers for diagnosis or prognosis of NKTCL needs
further exploration.
HACE1
HACE1, the novel E3 ubiquitin ligase mapping to the deletion region of 6q21 chromosome, inhibits cell
cycle progression via regulating the degradation of cyclin D1. As a tumor suppressor gene, it has been found