Page 120 - Read Online
P. 120
Page 224 Musumeci et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2020;4:221-37 I https://doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2020.22
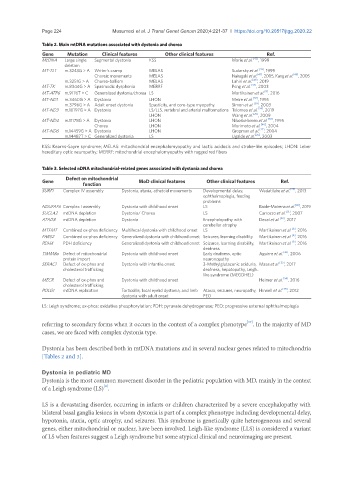
Table 2. Main mtDNA mutations associated with dystonia and chorea
Gene Mutation Clinical features Other clinical features Ref.
MtDNA Large single Segmental dystonia KSS Marie et al. [42] , 1999
deletion
MT-TL1 m.3243G > A Writer’s cramp MELAS Sudarsky et al. [43] , 1999
Choreic movements MELAS Nakagaki et al. [47] , 2005, Kang et al. [48] , 2005
m.3251G > A Chorea-ballism MELAS Lahiri et al. [49] , 2019
MT-TK m.8344G > A Spasmodic dysphonia MERRF Peng et al. [44] , 2003
[8]
MT-ATP6 m.9176T > C Generalized dystonia/chorea LS Martikainen et al. , 2016
MT-ND1 m.3460G > A Dystonia LHON Meire et al. [37] , 1995
m.3796G > A Adult onset dystonia Spasticity, and core-type myopathy. Simon et al. [39] , 2003
MT-ND3 m.10197G > A Dystonia LS/LLS, vertebral and arterial malformations Tolomeo et al. [24] , 2019
LHON Wang et al. [26] , 2009
MT-ND4 m.11178G > A Dystonia LHON Nikoskelainen et al. [38] , 1995
Chorea LHON Morimoto et al. [46] , 2004
MT-ND6 m.14459G > A Dystonia LHON Gropman et al. [27] , 2004
m.14487T > C Generalized dystonia LS Ugalde et al. [25] , 2003
KSS: Kearns-Sayre syndrome; MELAS: mitochondrial encephalomyopathy and lactic acidosis and stroke-like episodes; LHON: Leber
hereditary optic neuropathy; MERRF: mitochondrial encephalomyopathy with ragged red fibers
Table 3. Selected nDNA mitochondrial-related genes associated with dystonia and chorea
Defect on mitochondrial
Gene MoD clinical features Other clinical features Ref.
function
SURF1 Complex IV assembly Dystonia, ataxia, athetoid movements Developmental delay, Wedatilake et al. [29] , 2013
ophthalmoplegia, feeding
problems
NDUFAF6 Complex I assembly Dystonia with childhood onset LS Baide-Mairena et al. [30] , 2019
SUCLA2 mtDNA depletion Dystonia/ Chorea LS Carrozzo et al. [31] , 2007
ATAD3 mtDNA depletion Dystonia Encephalopathy with Desai et al. [32] , 2017
cerebellar atrophy
[8]
MTFMT Combined ox-phos deficiency Multifocal dystonia with childhood onset LS Martikainen et al. , 2016
[8]
FARS2 Combined ox-phos deficiency Generalized dystonia with childhood onset Seizures, learning disability Martikainen et al. , 2016
[8]
PDHX PDH deficiency Generalized dystonia with childhood onset Seizures, learning disability, Martikainen et al. , 2016
deafness
TIMM8a Defect of mitochondrial Dystonia with childhood onset Early deafness, optic Aguirre et al. [36] , 2006
protein import neuronopathy
SERAC1 Defect of ox-phos and Dystonia with infantile onset 3-Methylglutaconic aciduria, Maas et al. [33] , 2017
cholesterol trafficking deafness, hepatopathy, Leigh-
like syndrome (MEGDHEL)
MECR Defect of ox-phos and Dystonia with childhood onset Heimer et al. [34] , 2016
cholesterol trafficking
POLG1 mtDNA replication Torticollis, focal eyelid dystonia, and limb Ataxia, seizures, neuropathy, Hinnell et al. [45] , 2012
dystonia with adult onset PEO
LS: Leigh syndrome; ox-phos: oxidative phosphorylation; PDH: pyruvate dehydrogenase; PEO: progressive external ophthalmoplegia
[17]
referring to secondary forms when it occurs in the context of a complex phenotype . In the majority of MD
cases, we are faced with complex dystonia type.
Dystonia has been described both in mtDNA mutations and in several nuclear genes related to mitochondria
[Tables 2 and 3].
Dystonia in pediatric MD
Dystonia is the most common movement disorder in the pediatric population with MD, mainly in the context
[8]
of a Leigh syndrome (LS) .
LS is a devastating disorder, occurring in infants or children characterized by a severe encephalopathy with
bilateral basal ganglia lesions in whom dystonia is part of a complex phenotype including developmental delay,
hypotonia, ataxia, optic atrophy, and seizures. This syndrome is genetically quite heterogeneous and several
genes, either mitochondrial or nuclear, have been involved. Leigh-like syndrome (LLS) is considered a variant
of LS when features suggest a Leigh syndrome but some atypical clinical and neuroimaging are present.