Page 119 - Read Online
P. 119
Musumeci et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2020;4:221-37 I https://doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2020.22 Page 223
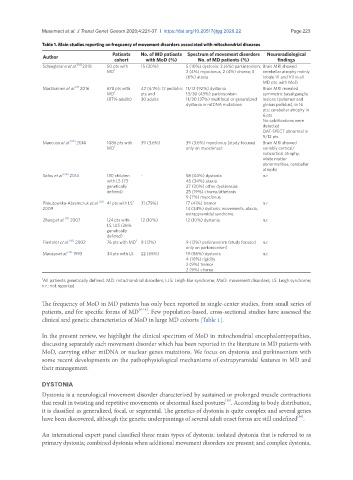
Table 1. Main studies reporting on frequency of movement disorders associated with mitochondrial diseases
Patients No. of MD patients Spectrum of movement disorders Neuroradiological
Author
cohort with MoD (%) No. of MD patients (%) findings
Schreglmann et al. [14] 2018 50 pts with 15 (30%) 5 (10%) dystonia; 3 (6%) parkinsonism; Brain MRI showed
MD 1 2 (4%) myoclonus, 2 (4%) chorea; 3 cerebellar atrophy mainly
(6%) ataxia lobule VI and VII in all
MD pts. with MoD
Martikainen et al. 2016 678 pts with 42 (6.1%): 12 pediatric 11/12 (92%) dystonia Brain MRI revealed
[8]
MD 1 pts and 13/30 (43%) parkinsonism symmetric basal ganglia
(87% adults) 30 adults 11/30 (37%) multifocal or generalized lesions (putamen and
dystonia in mtDNA mutations globus pallidus), in 16
pts; cerebellar atrophy in
6 pts
No calcifications were
detected
DAT-SPECT abnormal in
9/12 pts
Mancuso et al. [90] 2014 1086 pts with 39 (3.6%) 39 (3.6%) myoclonus (study focused Brain MRI showed
MD 1 only on myoclonus) variably cortical/
subcortical atrophy,
white matter
abnormalities, cerebellar
atrophy
Sofou et al. [20] 2014 130 children - 58 (44%) dystonia n.r.
with LS (73 45 (34%) ataxia
genetically 27 (20%) other dyskinesias
defined) 25 (19%) chorea/athetosis
9 (7%) myoclonus
Piekutowska-Abramczuk et al. [23] 41 pts with LS 1 31 (75%) 17 (41%) tremor n.r.
2009 14 (34%) dystonic movements, ataxia,
extrapyramidal syndrome
Zhang et al. [21] 2007 124 pts with 12 (10%) 12 (10%) dystonia n.r.
LS, LLS (26%
genetically
defined)
Finsterer et al. [50] 2002 76 pts with MD 1 9 (12%) 9 (12%) parkinsonism (study focused n.r.
only on parkinsonism)
Macaya et al. [12] 1993 34 pts with LS 22 (65%) 19 (86%) dystonia n.r.
4 (18%) rigidity
2 (9%) tremor
2 (9%) chorea
1 All patients genetically defined. MD: mitochondrial disorders; LLS: Leigh-like syndrome; MoD: movement disorders; LS: Leigh syndrome;
n.r.: not reported
The frequency of MoD in MD patients has only been reported in single-center studies, from small series of
patients, and for specific forms of MD [8-14] . Few population-based, cross-sectional studies have assessed the
clinical and genetic characteristics of MoD in large MD cohorts [Table 1].
In the present review, we highlight the clinical spectrum of MoD in mitochondrial encephalomyopathies,
discussing separately each movement disorder which has been reported in the literature in MD patients with
MoD, carrying either mtDNA or nuclear genes mutations. We focus on dystonia and parkinsonism with
some recent developments on the pathophysiological mechanisms of extrapyramidal features in MD and
their management.
DYSTONIA
Dystonia is a neurological movement disorder characterized by sustained or prolonged muscle contractions
[15]
that result in twisting and repetitive movements or abnormal fixed postures . According to body distribution,
it is classified as generalized, focal, or segmental. The genetics of dystonia is quite complex and several genes
[16]
have been discovered, although the genetic underpinnings of several adult onset forms are still undefined .
An international expert panel classified three main types of dystonia: isolated dystonia that is referred to as
primary dystonia; combined dystonia when additional movement disorders are present; and complex dystonia,