Page 93 - Read Online
P. 93
Cendrós et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2020;4:210-20 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2020.21 Page 213
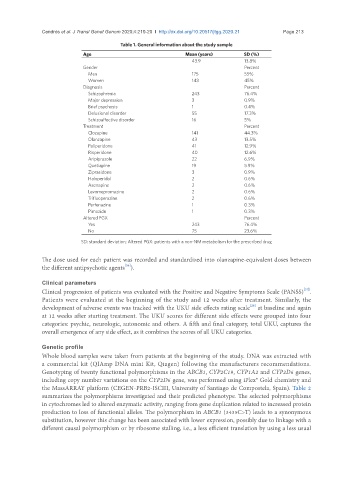
Table 1. General information about the study sample
Age Mean (years) SD (%)
43.9 13.8%
Gender Percent
Men 175 55%
Women 143 45%
Diagnosis Percent
Schizophrenia 243 76.4%
Major depression 3 0.9%
Brief psychosis 1 0.4%
Delusional disorder 55 17.3%
Schizoaffective disorder 16 5%
Treatment Percent
Clozapine 141 44.3%
Olanzapine 43 13.5%
Paliperidone 41 12.9%
Risperidone 40 12.6%
Aripiprazole 22 6.9%
Quetiapine 19 5.9%
Ziprasidone 3 0.9%
Haloperidol 2 0.6%
Asenapine 2 0.6%
Levomepromazine 2 0.6%
Trifluoperazine 2 0.6%
Perfenazine 1 0.3%
Pimozide 1 0.3%
Altered PGX Percent
Yes 243 76.4%
No 75 23.6%
SD: standard deviation; Altered PGX: patients with a non-NM metabolism for the prescribed drug
The dose used for each patient was recorded and standardized into olanzapine-equivalent doses between
[26]
the different antipsychotic agents ).
Clinical parameters
Clinical progression of patients was evaluated with the Positive and Negative Symptoms Scale (PANSS) .
[27]
Patients were evaluated at the beginning of the study and 12 weeks after treatment. Similarly, the
development of adverse events was tracked with the UKU side effects rating scale at baseline and again
[28]
at 12 weeks after starting treatment. The UKU scores for different side effects were grouped into four
categories: psychic, neurologic, autonomic and others. A fifth and final category, total UKU, captures the
overall emergence of any side effect, as it combines the scores of all UKU categories.
Genetic profile
Whole blood samples were taken from patients at the beginning of the study. DNA was extracted with
a commercial kit (QIAmp DNA mini Kit, Qiagen) following the manufacturers recommendations.
Genotyping of twenty functional polymorphisms in the ABCB1, CYP2C19, CYP1A2 and CYP2D6 genes,
including copy number variations on the CYP2D6 gene, was performed using iPlex® Gold chemistry and
the MassARRAY platform (CEGEN-PRB2-ISCIII, University of Santiago de Compostela, Spain). Table 2
summarizes the polymorphisms investigated and their predicted phenotype. The selected polymorphisms
in cytochromes led to altered enzymatic activity, ranging from gene duplication related to increased protein
production to loss of functionial alleles. The polymorphism in ABCB1 (3435C>T) leads to a synonymous
substitution, however this change has been associated with lower expression, possibly due to linkage with a
different causal polymorphism or by ribosome stalling, i.e., a less efficient translation by using a less usual