Page 47 - Read Online
P. 47
Bibi et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2024;8:119-161 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2023.50 Page 137
Table 1. Completed Phase 3 clinical trials of immune checkpoint inhibitors in Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer
(mCRPC)
Number of
Trial name/NCT ID Methodologies patients Trial Significant outcome
enrolled type
CA184-095/NCT01057810 Ipilimumab verses placebo 837 Phase Median OS 28.7 vs. 29.7 months. No improvement in OS
[251]
3 (Overall survival) with ipilimumab
CA184-43/NCT00861614 Ipilimumab vs. placebo 799 Phase Median OS 11, 2 months vs. 10, 0 months [252]
following radiotherapy 3
[253]
KEYNOTE-641/CT03834493 Pembrolizumab + 1244 Phase Primary endpoints were not met
enzalutamide vs. placebo + 3
enzalutamide in mCRPC
KEYNOTE-010/NCT03834519 Pembrolizumab + olaparib 793 Phase Median OS with Pembrolizumab + Olaparib was 15.8
vs. NHA in mCRPC 3 months (95%CI: 14.6-17.0) compared to 14.6 months
(95%CI: 12.6-17.3) in the control arm. The HR was 0.94
[254]
(95%CI: 0.77-1.14) with a P-value of 0.26
KEYNOTE-921/NCT03834506 Pembrolizumab + docetaxel 1030 Phase Median OS with Pembrolizumab + Docetaxel was 19.6
vs. docetaxel in mCRPC 3 months (95%CI: 18.2 to 20.9) compared to 19.0 months
(95%CI: 17.9 to 20.9) with Docetaxel alone. The HR was
[255]
0.92 (95%CI: 0.78-1.09) with a P-value of 0.1677 .
IMbassador250/NCT03016312 Atezolizumab + 772 Phase Median OS with atezolizumab + enzalutamide was 15.2
enzalutamide vs. placebo + 3 months (95%CI: 14.0-17.0) compared to 16.6 months
enzalutamide in mCRPC (95%CI: 14.7-18.4) in the control group. The HR was 1.12
(95%CI: 0.91-1.37) with a P-value of 0.28 [256] .
[257,258]
CheckMate-7DX Nivolumab + docetaxel vs. 984 Phase Primary endpoints were not met .
/NCT04100018 Placebo + docetaxel in 3
mCRPC
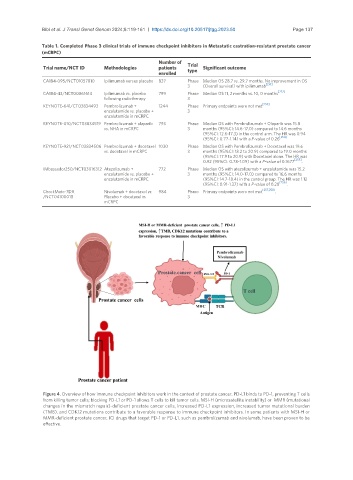
Figure 4. Overview of how immune checkpoint inhibitors work in the context of prostate cancer. PD-L1 binds to PD-1, preventing T cells
from killing tumor cells; blocking PD-L1 or PD-1 allows T cells to kill tumor cells. MSI-H (microsatellite instability) or MMR (mutational
changes in the mismatch repair)-deficient prostate cancer cells, increased PD-L1 expression, increased tumor mutational burden
(TMB), and CDK12 mutations contribute to a favorable response to immune checkpoint inhibitors. In some patients with MSI-H or
MMR-deficient prostate cancer, ICI drugs that target PD-1 or PD-L1, such as pembrolizumab and nivolumab, have been proven to be
effective.