Page 98 - Read Online
P. 98
Maher et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2023;7:94-109 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2023.04 Page 92
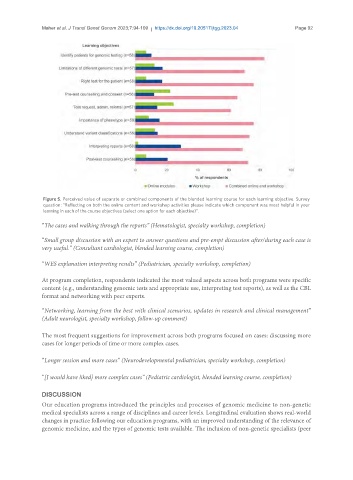
Figure 5. Perceived value of separate or combined components of the blended learning course for each learning objective. Survey
question: “Reflecting on both the online content and workshop activities please indicate which component was most helpful in your
learning in each of the course objectives (select one option for each objective)”.
“The cases and walking through the reports” (Hematologist, specialty workshop, completion)
“Small group discussion with an expert to answer questions and pre-empt discussion after/during each case is
very useful.” (Consultant cardiologist, blended learning course, completion)
“WES explanation interpreting results” (Pediatrician, specialty workshop, completion)
At program completion, respondents indicated the most valued aspects across both programs were specific
content (e.g., understanding genomic tests and appropriate use, interpreting test reports), as well as the CBL
format and networking with peer experts.
“Networking, learning from the best with clinical scenarios, updates in research and clinical management”
(Adult neurologist, specialty workshop, follow-up comment)
The most frequent suggestions for improvement across both programs focused on cases: discussing more
cases for longer periods of time or more complex cases.
“Longer session and more cases” (Neurodevelopmental pediatrician, specialty workshop, completion)
“[I would have liked] more complex cases” (Pediatric cardiologist, blended learning course, completion)
DISCUSSION
Our education programs introduced the principles and processes of genomic medicine to non-genetic
medical specialists across a range of disciplines and career levels. Longitudinal evaluation shows real-world
changes in practice following our education programs, with an improved understanding of the relevance of
genomic medicine, and the types of genomic tests available. The inclusion of non-genetic specialists (peer