Page 97 - Read Online
P. 97
Page 91 Maher et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2023;7:94-109 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2023.04
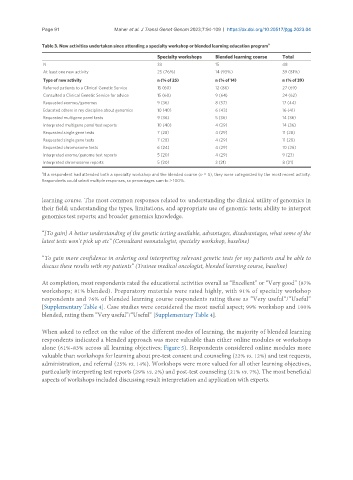
Table 3. New activities undertaken since attending a specialty workshop or blended learning education program a
Specialty workshops Blended learning course Total
N 33 15 48
At least one new activity 25 (76%) 14 (93%) 39 (81%)
Type of new activity n (% of 25) n (% of 14) n (% of 39)
Referred patients to a Clinical Genetic Service 15 (60) 12 (86) 27 (69)
Consulted a Clinical Genetic Service for advice 15 (60) 9 (64) 24 (62)
Requested exomes/genomes 9 (36) 8 (57) 17 (44)
Educated others in my discipline about genomics 10 (40) 6 (43) 16 (41)
Requested multigene panel tests 9 (36) 5 (36) 14 (36)
Interpreted multigene panel test reports 10 (40) 4 (29) 14 (36)
Requested single gene tests 7 (28) 4 (29) 11 (28)
Requested single gene tests 7 (28) 4 (29) 11 (28)
Requested chromosome tests 6 (24) 4 (29) 10 (26)
Interpreted exome/genome test reports 5 (20) 4 (29) 9 (23)
Interpreted chromosome reports 5 (20) 3 (21) 8 (21)
a
If a respondent had attended both a specialty workshop and the blended course (n = 5), they were categorized by the most recent activity.
Respondents could select multiple responses, so percentages sum to > 100%.
learning course. The most common responses related to: understanding the clinical utility of genomics in
their field; understanding the types, limitations, and appropriate use of genomic tests; ability to interpret
genomics test reports; and broader genomics knowledge.
“[To gain] A better understanding of the genetic testing available, advantages, disadvantages, what some of the
latest tests won’t pick up etc” (Consultant neonatologist, specialty workshop, baseline)
“To gain more confidence in ordering and interpreting relevant genetic tests for my patients and be able to
discuss these results with my patients” (Trainee medical oncologist, blended learning course, baseline)
At completion, most respondents rated the educational activities overall as “Excellent” or “Very good” (87%
workshops; 81% blended). Preparatory materials were rated highly, with 91% of specialty workshop
respondents and 76% of blended learning course respondents rating these as “Very useful”/“Useful”
[Supplementary Table 4]. Case studies were considered the most useful aspect; 99% workshop and 100%
blended, rating them “Very useful”/“Useful” [Supplementary Table 4].
When asked to reflect on the value of the different modes of learning, the majority of blended learning
respondents indicated a blended approach was more valuable than either online modules or workshops
alone (61%-83% across all learning objectives; Figure 5). Respondents considered online modules more
valuable than workshops for learning about pre-test consent and counseling (22% vs. 12%) and test requests,
administration, and referral (25% vs. 14%). Workshops were more valued for all other learning objectives,
particularly interpreting test reports (29% vs. 2%) and post-test counseling (21% vs. 7%). The most beneficial
aspects of workshops included discussing result interpretation and application with experts.