Page 30 - Read Online
P. 30
Xu et al. J Surveill Secur Saf 2020;1:16-33 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jsss.2020.04 Page 23
A B
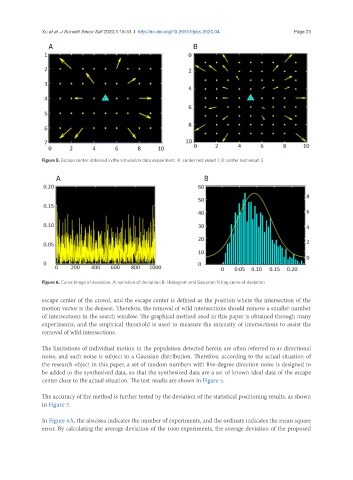
Figure 5. Escape center obtained in the simulation data experiment. A: center test result 1; B: center test result 2
A B
Figure 6. Curve image of deviation. A: variation of deviation; B: Histogram and Gaussian fitting curve of deviation
escape center of the crowd, and the escape center is defined as the position where the intersection of the
motion vector is the densest. Therefore, the removal of wild intersections should remove a smaller number
of intersections in the search window. The graphical method used in this paper is obtained through many
experiments, and the empirical threshold is used to measure the intensity of intersections to assist the
removal of wild intersections.
The limitations of individual motion in the population detected herein are often referred to as directional
noise, and such noise is subject to a Gaussian distribution. Therefore, according to the actual situation of
the research object in this paper, a set of random numbers with five-degree direction noise is designed to
be added to the synthesized data, so that the synthesized data are a set of known ideal data of the escape
center close to the actual situation. The test results are shown in Figure 5.
The accuracy of the method is further tested by the deviation of the statistical positioning results, as shown
in Figure 5.
In Figure 6A, the abscissa indicates the number of experiments, and the ordinate indicates the mean square
error. By calculating the average deviation of the 1000 experiments, the average deviation of the proposed