Page 18 - Read Online
P. 18
Schmidt et al. J Surveill Secur Saf 2020;1:1-15 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jsss.2019.02 Page 11
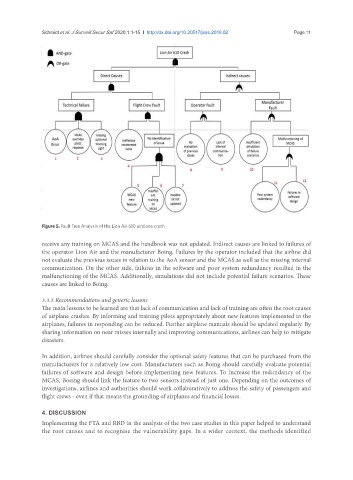
Figure 5. Fault Tree Analysis of the Lion Air 610 airplane crash
receive any training on MCAS and the handbook was not updated. Indirect causes are linked to failures of
the operator Lion Air and the manufacturer Boing. Failures by the operator included that the airline did
not evaluate the previous issues in relation to the AoA sensor and the MCAS as well as the missing internal
communication. On the other side, failures in the software and poor system redundancy resulted in the
malfunctioning of the MCAS. Additionally, simulations did not include potential failure scenarios. These
causes are linked to Boing.
3.3.5 Recommendations and generic lessons
The main lessons to be learned are that lack of communication and lack of training are often the root causes
of airplane crashes. By informing and training pilots appropriately about new features implemented in the
airplanes, failures in responding can be reduced. Further airplane manuals should be updated regularly. By
sharing information on near misses internally and improving communications, airlines can help to mitigate
disasters.
In addition, airlines should carefully consider the optional safety features that can be purchased from the
manufacturers for a relatively low cost. Manufacturers such as Boing should carefully evaluate potential
failures of software and design before implementing new features. To increase the redundancy of the
MCAS, Boeing should link the feature to two sensors instead of just one. Depending on the outcomes of
investigations, airlines and authorities should work collaboratively to address the safety of passengers and
flight crews - even if that means the grounding of airplanes and financial losses.
4. DISCUSSION
Implementing the FTA and RBD in the analysis of the two case studies in this paper helped to understand
the root causes and to recognise the vulnerability gaps. In a wider context, the methods identified