Page 17 - Read Online
P. 17
Page 10 Schmidt et al. J Surveill Secur Saf 2020;1:1-15 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jsss.2019.02
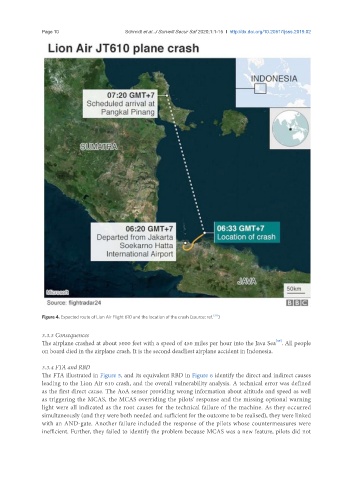
Figure 4. Expected route of Lion Air Flight 610 and the location of the crash (source: ref. [37] )
3.3.3 Consequences
[39]
The airplane crashed at about 5000 feet with a speed of 450 miles per hour into the Java Sea . All people
on board died in the airplane crash. It is the second deadliest airplane accident in Indonesia.
3.3.4 FTA and RBD
The FTA illustrated in Figure 5, and its equivalent RBD in Figure 6 identify the direct and indirect causes
leading to the Lion Air 610 crash, and the overall vulnerability analysis. A technical error was defined
as the first direct cause. The AoA sensor providing wrong information about altitude and speed as well
as triggering the MCAS, the MCAS overriding the pilots’ response and the missing optional warning
light were all indicated as the root causes for the technical failure of the machine. As they occurred
simultaneously (and they were both needed and sufficient for the outcome to be realised), they were linked
with an AND-gate. Another failure included the response of the pilots whose countermeasures were
inefficient. Further, they failed to identify the problem because MCAS was a new feature, pilots did not