Page 106 - Read Online
P. 106
Mooraj et al. J Mater Inf 2023;3:4 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jmi.2022.41 Page 31 of 45
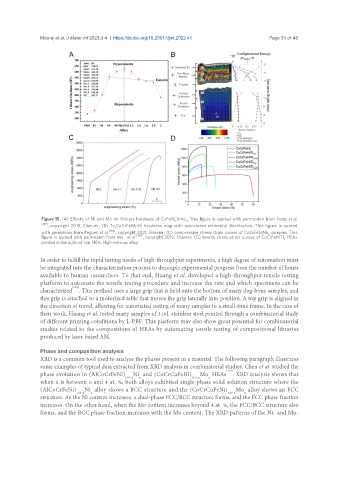
Figure 15. (A) Effects of Ni and Mo on Vickers hardness of CoFeNi Vmo . This figure is quoted with permission from Jiang et al.
x y
[187]
, copyright 2015, Elsevier; (B) Ta CoCrFeMnNi hardness map with associated elemental distribution. This figure is quoted
x
with permission from Pegues et al. [166] , copyright 2021, Elsevier; (C) compressive stress-strain curves of CoCrFeNiNb samples. This
[188] x
figure is quoted with permission from Ma et al. , copyright 2012, Elsevier; (D) tensile stress-strain curves of CoCrFeNiTi HEAs
x
printed in the authors’ lab. HEA: High-entropy alloy.
In order to fulfill the rapid testing needs of high-throughput experiments, a high degree of automation must
be integrated into the characterization process to decouple experimental progress from the number of hours
available to human researchers. To that end, Huang et al. developed a high-throughput tensile testing
platform to automate the tensile testing procedure and increase the rate and which specimens can be
[192]
characterized . This method uses a large grip that is held onto the bottom of many dog-bone samples, and
this grip is attached to a motorized table that moves the grip laterally into position. A top grip is aligned in
the direction of travel, allowing for automated testing of many samples in a small-time frame. In the case of
their work, Huang et al. tested many samples of 316L stainless steel printed through a combinatorial study
of different printing conditions by L-PBF. This platform may also show great potential for combinatorial
studies related to the compositions of HEAs by automating tensile testing of compositional libraries
produced by laser-based AM.
Phase and composition analysis
XRD is a common tool used to analyze the phases present in a material. The following paragraph illustrates
some examples of typical data extracted from XRD analysis in combinatorial studies. Chen et al. studied the
[193]
phase evolution in (AlCoCrFeNi) Ni and (CoCrCuFeNi) Mo HEAs . XRD analysis shows that
100-x x 100-x x
when x is between 0 and 4 at. %, both alloys exhibited single-phase solid solution structure where the
(AlCoCrFeNi) Ni alloy shows a BCC structure and the (CoCrCuFeNi) Mo alloy shows an FCC
100-x x 100-x x
structure. As the Ni content increases, a dual-phase FCC/BCC structure forms, and the FCC phase fraction
increases. On the other hand, when the Mo content increases beyond 4 at. %, the FCC/BCC structure also
forms, and the BCC phase fraction increases with the Mo content. The XRD patterns of the Ni- and Mo-